-
Factory Environmental Governance Comprehensive Solution Provider
-
Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment

Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment
————— ◆ Industrial exhaust gas analysis ◆ —————
>> Overview of spray paint exhaust
The exhaust gas of spray painting comes from the volatilization of organic solvents and diluents used in spray painting operations, and the organic solvents will not adhere to the surface of the spray paint with the paint, and will be completely released to form organic exhaust gas during the spray painting and curing process. The amount of xylene vapour emitted during the spraying process accounts for about 30% of the amount of diluent, and another 70% is volatilized during the drying process. The suspended particles formed by atomizing the organic solvent during spray painting are easily radiated to the surrounding air and pollute the air. The main methods of collecting and processing paint mist in polluted air, improving the paint spraying environment, and meeting environmental protection emission requirements.
>>Paint exhaust gas composition
Spraying exhaust gas is the exhaust gas generated when spraying paint. The components of spraying exhaust gas and drying exhaust gas are as follows:
benzene, toluene, xylene, hexane, heptane, methyl ethyl ketone, ethyl acetate, carbon tetrachloride Etc., mainly the treatment of "triphenyls" and volatile organic waste gases (VOCs).
————— ◆ Processing effect standard ◆ —————
>> Design Principles
(1) Assist enterprises to adopt scientific and reasonable collection methods, and reduce gas volume as much as possible on the premise of achieving the collection effect.
(2) Actively and steadily adopt new technologies and new equipment, and adopt advanced and reliable pollution control technology in accordance with the status quo and management level of the enterprise, and strive to achieve stable operation, low cost, convenient management, and easy maintenance, so as to completely eliminate exhaust gas pollution and protect Environmental purpose. (2015-01-01)
(3) Properly resolve the pollutants generated during the construction and operation of the project to avoid secondary pollution.
(4) Strictly implement current national, local, and other codes, regulations, and standards on fire prevention, safety, health, and environmental protection.
(5) Select new, high-efficiency, low-noise equipment, pay attention to energy saving and consumption reduction.
(6) The overall plan layout strives to be compact, reasonably smooth, simple and practical. Minimize project occupation and construction difficulty.
(7) Strictly implement relevant national design codes and standards, and pay attention to fire protection and safety work. (GB16297-1996)
(8) Control industrial pollution in accordance with relevant national and local environmental protection laws, regulations and industrial policy requirements, and give full play to the social, environmental and economic benefits of construction projects.
>> Project scope and standards
1. Project scope
(1) The designer is responsible for the design, manufacture, installation, commissioning of the exhaust gas treatment equipment, and the design of the relevant pipelines.
(2) The designer is responsible for training the equipment operator of the owner unit.
(3) The owner unit is responsible for the supporting public works of the project, including power supply, water vapor, compressed air, circulating cooling water, etc.
2.Technical requirements
(1) The project does not consider land acquisition and uses the original factory land, which cannot seriously affect production;
(2) Adopt mature exhaust gas treatment technology, which requires technology to be safe, reliable, and economically reasonable;
(3) The disposal of by-products should not cause secondary pollution;
(4) All equipment and materials are new;
(5) Simple observation, monitoring and maintenance;
(6) Ensure personnel and equipment safety;
(7) Save energy, water and raw materials;
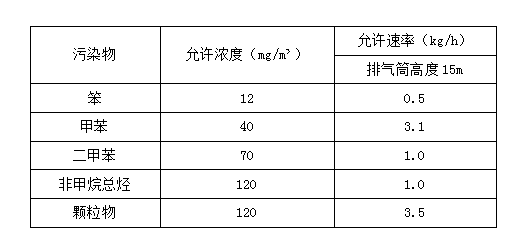
>> Emission Standard
Exhaust gas emission standards implement secondary standards, refer to the "Integrated Emission Standards for Air Pollutants" (GB16297-1996) and "Emission Standards for Odor Pollutants" (GB14554-93). The exhaust gas emission standards are as follows:
————— ◆ Basis for program customization ◆ —————
(1) Project-related information provided by the owner
(2) Environmental Protection Law of the People's Republic of China (2015-01-01)
(3) Law of the People's Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Atmospheric Pollution (2016-01-01)
(4) Ambient air quality standard (GB3095-2012)
(5) Decree No. 72 of the President of the People's Republic of China on the Law of the People's Republic of China on Cleaner Production Promotion
(6) "National 13th Five-Year Plan"
(7) "Integrated Emission Standard of Air Pollutants" (GB16297-1996)
(8) Emission Standard of Odor Pollutants (GB14554-1993)
(9) "Code for Environmental Protection Design of Construction Projects" (GB50483-2009)
(10) Design Code for Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning (GB50019-2003)
(11) Code for Fire Protection of Building Design (GB50016-2014)
(12) Design Specification for Power Supply and Distribution System (GB50052-2009)
(13) "Control Standards for Emissions of Volatile Organic Compounds in Industrial Enterprises" DB13 / 2322-2016
(14) Guangzhou Puhua Environmental Technology Co., Ltd.'s comprehensive experience based on years of exhaust gas treatment project engineering and technology research and development
————— ◆ Exhaust gas system design ◆ —————
The paint spraying waste gas to be treated considers operating cost and safety. The process route of this solution is planned to adopt " catalytic combustion + activated carbon adsorption desorption + blower " for effective waste gas treatment. The process equipment diagram is as follows:
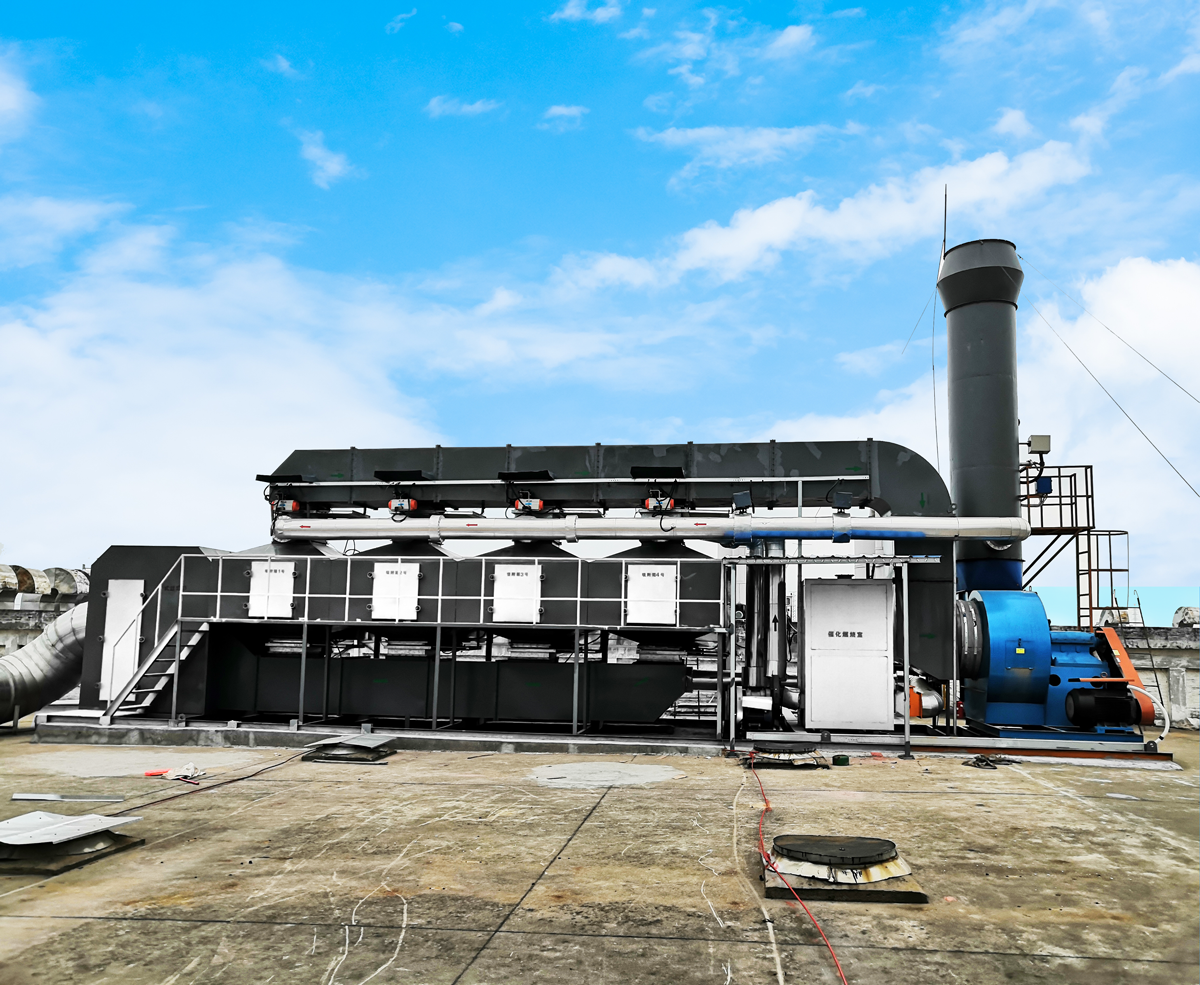

Dry filtration (spray washing) + activated carbon adsorption desorption + catalytic combustion + fan
(1) After the exhaust gas is pretreated to remove dust and particulate matter, it is sent to the activated carbon adsorber I and II. When the activated carbon adsorber I is near saturation, the processing gas is automatically switched to the activated carbon adsorber II (the activated carbon adsorber I stops). (Adsorption operation), and then the activated carbon adsorber I is desorbed and desorbed with a hot air flow to desorb organic matter from the activated carbon. During the desorption process, the organic waste gas has been concentrated, and its concentration has been increased by several tens of times compared to the original, reaching more than 2000 ppm. The concentrated waste gas is sent to the catalytic decomposition device, and is finally discharged as CO2 and H2O.
(2) After the completion of desorption and desorption, the activated carbon adsorber Ⅰ enters the standby state. When the activated carbon adsorber Ⅱ is close to saturation, the system will automatically switch back and desorb and desorb the activated carbon adsorber Ⅱ at the same time.
(3) When the concentration of organic waste gas reaches more than 2000ppm, spontaneous combustion can be maintained in the catalytic bed without external heating. This solution not only greatly saves energy consumption, but also reduces the equipment investment because the processing capacity of the catalytic cracker requires only 1/5 (60,000 m3 / h) of the original exhaust gas treatment capacity. This solution is suitable for both continuous work and intermittent work.
————— ◆ Cooperation Process ◆ —————