-
Factory Environmental Governance Comprehensive Solution Provider
-
Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment

Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment
————— ◆ Industrial exhaust gas analysis ◆ —————
>> Gas waste gas source
(1) During the accumulation of garbage, due to poor ventilation and the action of microorganisms, a certain amount of odorous gases such as ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, organic amines, and methane are generated, which are commonly referred to as garbage odor.
(2) The pollutants generated during the waste incineration process mainly include four categories: particulate matter (smoke), acid gases (CO, NOX, SO2, HCl, etc.), heavy metals (Hg, Cr, Pb, etc.) and organic pollutants (mainly Factor is dioxin).
1) HCl is derived from chlorine-containing waste in domestic waste.
2) SO2 originates from the high temperature oxidation process of sulfur-containing domestic waste.
3) NOX originates from the oxidation reaction of N2 and O2 and the combustion of nitrogen-containing organic matter during the incineration process of domestic garbage, 95% of which is NO, and the proportion of NO2 is very small.
4) CO is produced by incomplete combustion of organic combustibles in domestic waste.
5) Metal pollutants originate from heavy metals and compounds contained in domestic waste during incineration.
6) The production mechanism of organic pollutants is very complicated. Dioxin is the most toxic compound among them.
————— ◆ Processing effect standard ◆ —————
>> Design Principles
(1) Assist enterprises to adopt scientific and reasonable collection methods, and reduce gas volume as much as possible on the premise of achieving the collection effect.
(2) Actively and steadily adopt new technologies and new equipment, and adopt advanced and reliable pollution control technology in accordance with the status quo and management level of the enterprise, and strive to achieve stable operation, low cost, convenient management, and easy maintenance, so as to completely eliminate exhaust gas pollution and protect Environmental purpose. (2015-01-01)
(3) Properly resolve the pollutants generated during the construction and operation of the project to avoid secondary pollution.
(4) Strictly implement current national, local, and other codes, regulations, and standards on fire prevention, safety, health, and environmental protection.
(5) Select new, high-efficiency, low-noise equipment, pay attention to energy saving and consumption reduction.
(6) The overall plan layout strives to be compact, reasonably smooth, simple and practical. Minimize project occupation and construction difficulty.
(7) Strictly implement relevant national design codes and standards, and pay attention to fire protection and safety work. (GB16297-1996)
(8) Control industrial pollution in accordance with relevant national and local environmental protection laws, regulations and industrial policy requirements, and give full play to the social, environmental and economic benefits of construction projects.
>> Project scope and standards
1. Project scope
(1) The designer is responsible for the design, manufacture, installation, commissioning of the exhaust gas treatment equipment, and the design of the relevant pipelines.
(2) The designer is responsible for training the equipment operator of the owner unit.
(3) The owner unit is responsible for the supporting public works of the project, including power supply, water vapor, compressed air, circulating cooling water, etc.
2.Technical requirements
(1) The project does not consider land acquisition and uses the original factory land, which cannot seriously affect production;
(2) Adopt mature exhaust gas treatment technology, which requires technology to be safe, reliable, and economically reasonable;
(3) The disposal of by-products should not cause secondary pollution;
(4) All equipment and materials are new;
(5) Simple observation, monitoring and maintenance;
(6) Ensure personnel and equipment safety;
(7) Save energy, water and raw materials;
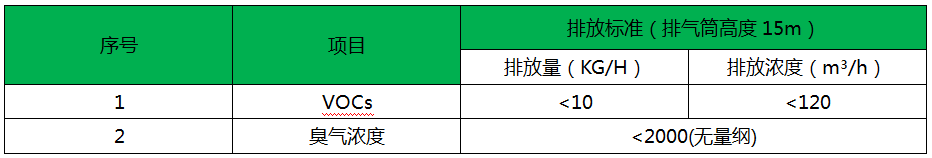
>> Emission Standard
The exhaust gas emission standards implement the secondary standards of the Comprehensive Emission Standard for Air Pollutants (GB16297-1996) and the Emission Standard for Odors (GB14554-93). The emission standards are as follows:
————— ◆ Basis for program customization ◆ —————
(1) Project-related information provided by the owner
(2) Environmental Protection Law of the People's Republic of China (2015-01-01)
(3) Law of the People's Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Atmospheric Pollution (2016-01-01)
(4) Ambient air quality standard (GB3095-2012)
(5) Decree No. 72 of the President of the People's Republic of China on the Law of the People's Republic of China on Cleaner Production Promotion
(6) "National 13th Five-Year Plan"
(7) "Integrated Emission Standard of Air Pollutants" (GB16297-1996)
(8) Emission Standard of Odor Pollutants (GB14554-1993)
(9) "Code for Environmental Protection Design of Construction Projects" (GB50483-2009)
(10) Design Code for Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning (GB50019-2003)
(11) Code for Fire Protection of Building Design (GB50016-2014)
(12) Design Specification for Power Supply and Distribution System (GB50052-2009)
(13) "Control Standards for Emissions of Volatile Organic Compounds in Industrial Enterprises" DB13 / 2322-2016
(14) Guangzhou Puhua Environmental Technology Co., Ltd.'s comprehensive experience based on years of exhaust gas treatment project engineering and technology research and development
————— ◆ Exhaust gas system design ◆ —————
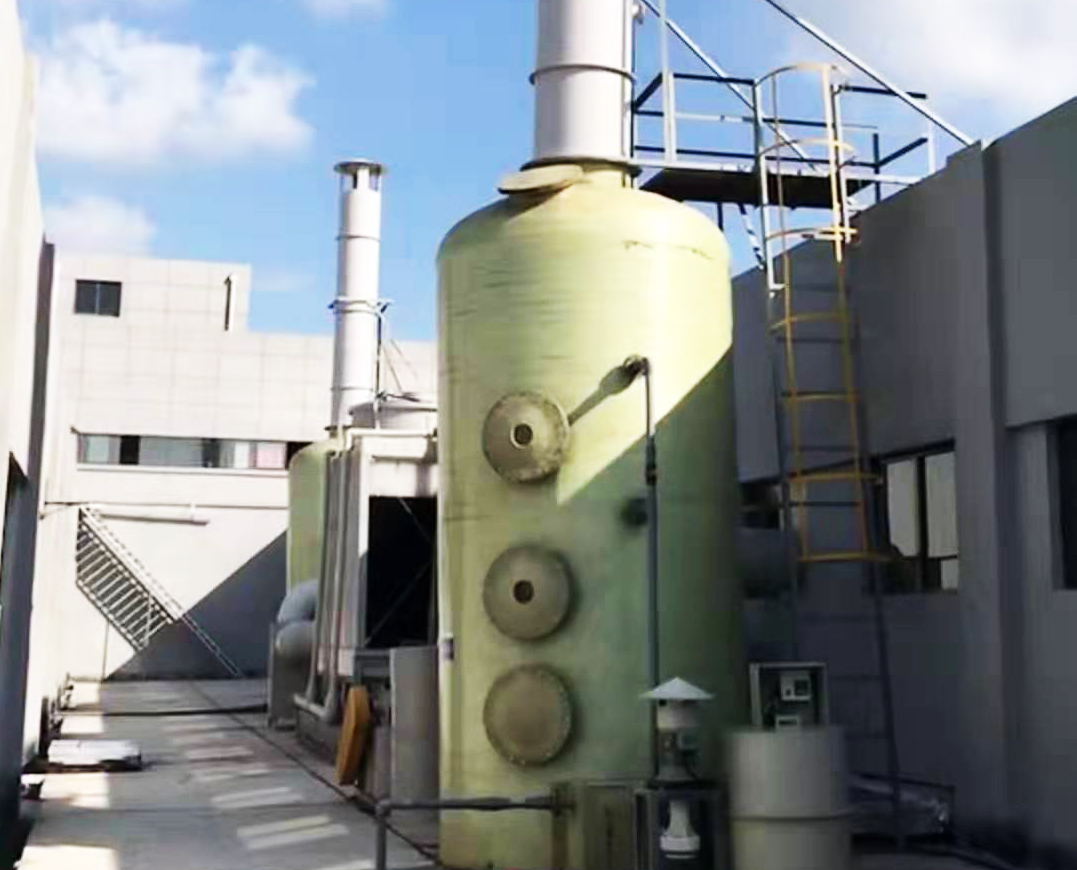
>> Sewage and waste gas treatment process
Considering the operating cost and safety of garbage odor treatment, the process adopts "ventilation system (pipe, induced draft fan) + core purification system (spray tower + UV photolysis purification equipment + activated carbon adsorption)" as the core process to treat garbage odor The process equipment diagram is as follows:
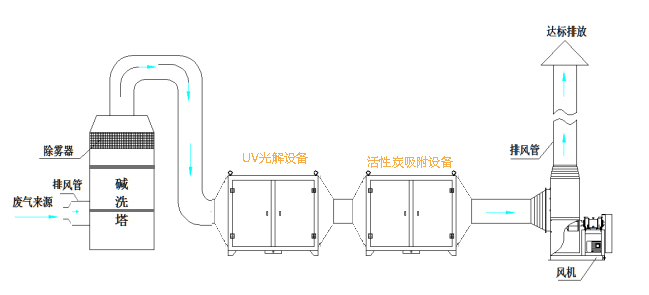
(1) The exhaust odor collected by the gas collection hood is introduced into the purification tower through the air duct, and the exhaust gas and water undergo full gas-liquid two-phase absorption and neutralization reaction through the filler layer. Gases such as ammonia and hydrogen sulfide are easily soluble in water. After the exhaust odor is purified, it is dewatered and defogged by the demister plate, and then enters the next process.
(2) The exhaust gas enters the core purification system (UV photolysis purification equipment). The UV photolysis purification equipment emits a special high-energy UV light beam to decompose oxygen molecules in the air to generate free oxygen (ie, active oxygen). At the same time, the high-energy UV light beam and Ozone performs synergistic photolysis and oxidation of organic waste gas and odor, and degrades and converts odorous gas into low-molecular compounds, water, and carbon dioxide. At the same time, it uses activated carbon adsorption as a processing device to achieve high-altitude emissions.
————— ◆ Cooperation Process ◆ —————











