-
Factory Environmental Governance Comprehensive Solution Provider
-
Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment

Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment
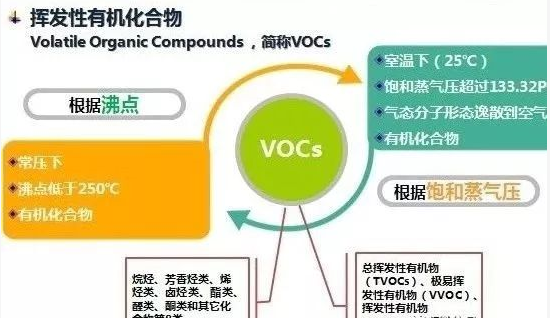
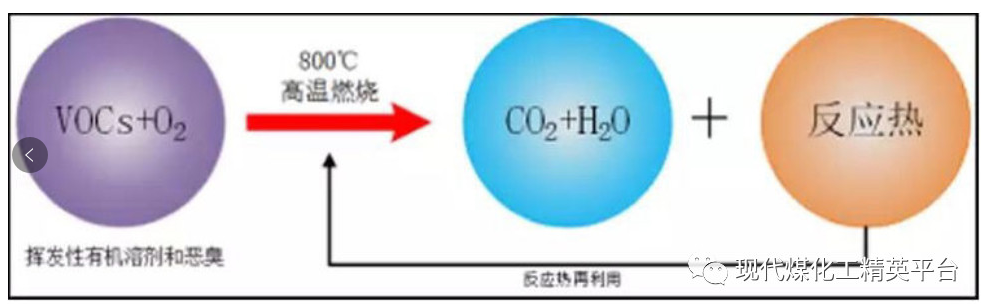
VOCs emissions have approached or exceeded NOx emissions, with annual emissions exceeding 20 million tons, which is the focus of supervision and treatment. It is mainly derived from the production and use of solvents, chemical and pharmaceutical production, transportation and loading of fuel oil, and vehicle exhaust emissions.
At present, there are various treatment methods for VOCs exhaust gas, including condensation recovery, high boiling point solvent absorption, activated carbon adsorption, and incineration disposal. According to the characteristics and economics of VOCs exhaust gas generation, RTO (Regeneration Chamber Oxidizer) technology has the advantages of high purification efficiency, thorough pollutant decomposition, high heat exchange efficiency, energy saving, low resistance, and low installed power of fans. Wide application prospects.
Compared with traditional catalytic combustion and direct-fired thermal oxidation furnaces, it has high thermal efficiency (90% or more), low operating cost, and can handle large air volumes and low concentrations (relative to exhaust emissions). There are two-chamber, three-chamber and multi-chamber RTO devices. The removal rate of VOCs in two-chamber RTO devices is 95% to 98%, and the removal rate of VOCs in three-chamber RTO devices can reach more than 98%.
The two-chamber RTO has no purge process. When the valve is switched, part of the VOCs exhaust gas is directly discharged without treatment, which reduces the removal efficiency of VOCs. Multi-chamber RTO is to increase the number of heat storage chambers for simultaneous intake and exhaust in order to ensure the uniformity of exhaust gas intake when the amount of exhaust gas is very large. At present, three-room RTO is a mainstream practical device, which takes into consideration both efficiency and investment cost.
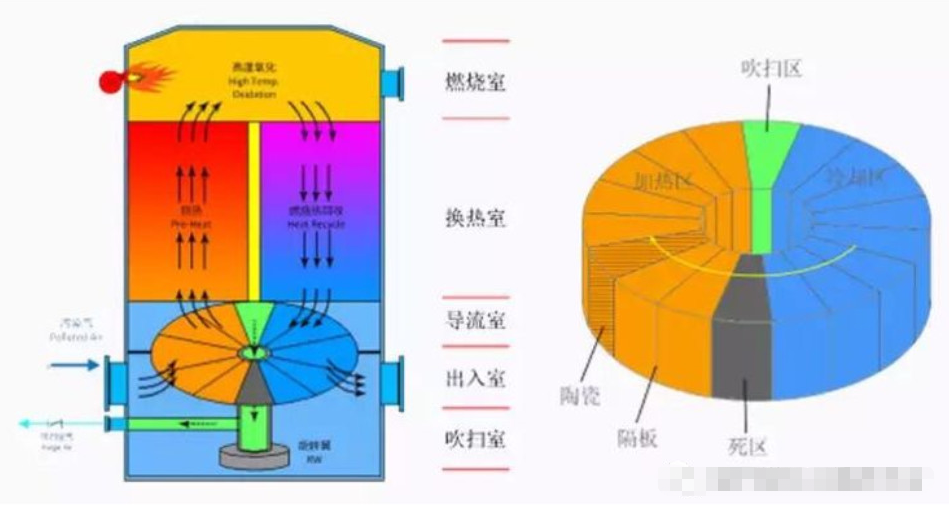
Three-Room RTO Operating Principle
The main structure of the three-chamber RTO consists of a combustion chamber, three ceramic packed beds, and six switching valves. When the organic exhaust gas enters the ceramic bed 1, the ceramic bed 1 exotherms, and the organic exhaust gas is heated to a certain temperature and then enters the combustion chamber for combustion. The high-temperature gas passes through the ceramic packed bed 2, the ceramic bed 2 absorbs heat and stores heat. After the high-temperature gas is cooled by the packed bed 2, it is discharged through a switching valve, and the packed bed 3 is purged to ensure that the unreacted exhaust gas that originally entered the packed bed 3 is not reacted. Combustion into the combustion chamber instead of direct emissions. After a period of time, the valve is switched, and the exhaust gas enters from packed bed 2, the packed bed 2 releases heat, packed bed 3 stores heat, and packed bed 1 is purged; then the air is fed into packed bed 3, and packed bed 1 stores heat, and packed bed 2 Perform a purge; this can be switched periodically to continuously treat organic waste gas. Three-Room RTO Operating Principle
Because RTO devices often use open flames to work, it is easy to cause explosion accidents, which is a more concerned issue when using RTO devices. Exhaust gas safety pre-treatment measures mainly include: (1) Concentration control: For safety reasons to prevent explosion or fire, the concentration of VOCs in the exhaust gas should generally be controlled below 25% LEL (lower explosive concentration limit); (2) Tempering control: To prevent tempering, the minimum flow rate of the exhaust gas should always be greater than the tempering speed when designing the pipe size, and an appropriate safety factor should be selected; (3) Safety measures: Venturi flame arresters, tempering preventers, and safety fluids can be adopted Safety control measures such as sealing, air dilution and non-tempering spray; (4) alarm chain: set explosion or tempering alarm instrument and safety interlock control system.
After years of operation and improvement, the RTO device has the following performance advantages:
(1) Almost all waste gas containing organic compounds can be processed, and organic waste gas with large air volume and low concentration (relative to direct combustion incinerator) can be processed;
(2) It can adapt to changes and fluctuations in the composition and concentration of VOCs in the exhaust gas;
(3) Insensitive to small amounts of dust and solid particles entrained in the exhaust gas;
(4) the highest thermal efficiency (> 90%) of all thermal combustion purification methods; (5) self-heating operation without the need for additional combustion under appropriate exhaust gas concentration conditions;
(6) High purification efficiency (three rooms> 98%, two rooms 95% ~ 98%), less maintenance work, safe and reliable operation;
(7) Organic deposits can be removed periodically and the heat storage body can be replaced;
(8) The pressure loss of the entire device is small (the total pressure loss of the RTO device system is generally <3 000 pa, which varies with the type of heat storage body used and the gas velocity), and the device has a long service life.
The main disadvantages are: (1) the device has a large weight (because of ceramic heat storage body) and a large volume; (2) requires continuous operation as much as possible; (3) the investment cost is relatively high; (4) for large air volume and low concentration exhaust In terms of operation costs, it is still high; (5) There is a certain risk of fire and explosion, the quality of domestic instruments is not high, and the prices of foreign brands are expensive.
(1) There have been multiple explosion accidents in the RTO device that treats petroleum ether-containing exhaust gas and the RTO device that treats isopropyl ether-containing exhaust gas, although the treatment concentration is significantly lower than the lower explosion limit. According to the analysis of the RTO survey, petroleum ether and isopropyl ether have the characteristics of low flash point and strong volatility. Therefore, RTO treatment of VOCs waste gas must pay attention to low flash point substances (petroleum ether, isopropyl ether, diethyl ether, cyclohexane, etc.); it is recommended that low flash point VOCs do not enter the RTO treatment device and be treated by carbon fiber adsorption alone.
(2) RTO device operation control parameters are relatively single. The main operating parameter currently monitored is the temperature of the combustion chamber. The feedback data from the online monitoring instrument for the concentration of intake VOCs is not accurate, so the combustion support amount of the combustion-supporting fuel cannot be determined in advance, which causes fluctuations in the combustion chamber temperature. When the concentration of VOCs is too high, the temperature of the combustion chamber is too high, which may cause damage to the heat storage body and reduce the service life of the RTO device. At present, the quality of domestic RTO instruments is not sufficient, and most of them cannot meet the requirements of operation management.
(3) Most units that use VTOs to treat VOCs exhaust gas are companies producing or using hazardous chemicals. They are particularly worried about explosion during use. Due to the lack of operational research, design specifications, and online monitoring data of RTO devices, for safety reasons, the current RTO device operating companies are conservative in the types and concentrations of VOCs exhaust gases.
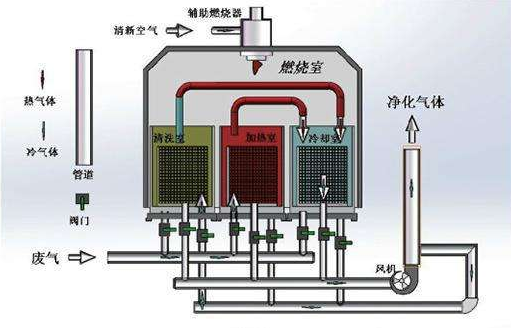
According to the investigation and relevant information, the three-chamber RTO device can take into account the processing efficiency and economic requirements; generally, when the design exhaust gas treatment air volume is 10 000 ~ 30 000 m3 / h, the floor area, design, material requirements, equipment installation, operation control Other aspects are more applicable, especially the small air volume and large air volume are not suitable for the three-chamber RTO. The annual operating cost of an RTO device is generally between several hundred thousand to several million, and the combustion-supporting fuel is natural gas or diesel or waste solvent. It is required that the concentration of VOCs exhaust gas entering the RTO device is between 1 000 and 8 000 mg / m3 to have obvious economic feasibility. According to the analysis of relevant data, when the concentration of VOCs reaches more than 2 000 mg / m3, the RTO device can work normally without using combustion-supporting fuel. run. Therefore, for the normal and stable operation of the supporting RTO device, the collection system for collecting VOCs must be sealed, rationalized and systematically designed, so as to ensure that the concentration of VOCs exhaust gas integrated into the RTO device is within a suitable range. The RTO device is designed to have a combustion chamber temperature above 850 ° C and an actual operating temperature above 720 ° C. Under the premise of ensuring the VOCs removal rate, properly reducing the combustion chamber temperature can reduce the amount of combustion fuel and reduce operating costs. The heat utilization efficiency of the RTO device is more than 90%, and the VOCs removal rate of the three-room RTO can reach more than 99%. The pressure loss of the entire RTO system is generally less than 3 000 Pa. Through the analysis of the RTO (Regenerative Thermal Oxidation Furnace) device, understand its principle, advantages, disadvantages, and problems, and provide a reference for the improvement, construction, and operation of the RTO device. RTO has the advantages of relatively high VOCs removal rate, high degree of automation, and convenient operation and management, but it also has certain restrictions and constraints.

In terms of safety, economy, and VOCs removal effect, RTO device is more suitable for treating exhaust gas with VOCs concentration of 1 000 ~ 8 000 mg / m3; if the concentration is too low, the removal efficiency is reduced, and more combustion-supporting fuel is required, and the economy is reduced ; The concentration is too high, exceeding the RTO design temperature, it is easy to damage the heat storage body, and even a fire accident occurs. The three-chamber RTO device (with an exhaust gas treatment capacity of 10 000 to 30 000 m3 / h) can take into account both the treatment efficiency and economic requirements, and is a reliable and applicable method for VOCs exhaust gas treatment.