-
Factory Environmental Governance Comprehensive Solution Provider
-
Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment

Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment
A few days ago, the Ministry of Environmental Protection issued "Principles and Methods for Setting National Emission Standards of Air Pollutants from Fixed Sources (Draft for Comment)" and "Principles and Methods for Setting Standards for Local Air Pollutant Emissions (Consultation Draft)". The full text is as follows:
National fixed source air pollutant emission standards
Develop principles and methods
Principles and methods for the development of national
Emission standards of air pollutants from stationary sources
(Consultation Draft)
Foreword
In order to implement the "Environmental Protection Law of the People's Republic of China" and "The Law of the People's Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Air Pollution", implement the "Administrative Measures for the Preparation and Revision of National Environmental Protection Standards" and "Guidance Opinions on Strengthening the Preparation and Revision of National Pollutant Discharge Standards" Work to formulate and revise the emission standards of source atmospheric pollutants and formulate this standard.
This standard specifies the basic principles, working procedures and technical routes for the formulation of national fixed source air pollutant emission standards, as well as the standard text structure and technical content requirements, and regulates the technical content determination of emission control requirements, compliance technology, monitoring methods, and determination of compliance. The principle method stipulates the content requirements for standard preparation instructions and technical reports.
This standard is issued for the first time.
Appendix A and Appendix B of this standard are informative appendices.
This standard is formulated by the Department of Science and Technology Standards of the Ministry of Environmental Protection.
The main drafting organization of this standard: Chinese Academy of Environmental Sciences.
This standard was approved by the Ministry of Environmental Protection on the ���������� date of 2017.
This standard will be implemented from 2018 ����������.
This standard is explained by the Ministry of Environmental Protection.
Principles and methods for establishing national fixed source air pollutant emission standards
This standard specifies the basic principles, working procedures and technical routes for the formulation of national standards for the discharge of atmospheric pollutants from fixed sources, as well as the basic technical methods for determining the structure of the standard text and the main technical content requirements, the main content requirements for the preparation of standards and technical reports.
This standard applies to the formulation and revision of national standards for air pollutant emissions from fixed sources of pollution. The technical content of local fixed source air pollutant emission standards can be determined with reference to this standard.
The content of this standard refers to the following documents or clauses therein. For undated references, the valid version is applicable to this standard.
GB 14554 Emission Standard for Odor Pollutants
GB / T 16157 Determination of particulate matter in exhaust gas from stationary sources and sampling methods for gaseous pollutants
HJ / T 55 Technical guidelines for fugitive emissions monitoring of air pollutants
HJ 168 Technical Guidelines for the Preparation and Revision of Environmental Monitoring Analysis Methods Standards
HJ / T 397 Fixed source exhaust gas monitoring technical specifications
HJ 565 Technical Guidelines for the Preparation and Publication of Environmental Protection Standards
HJ ������ Principles and methods for setting local air pollutant emission standards
HJ ������ Guidelines for the preparation of best environmental protection technology guidelines for environmental protection
`` Guidelines for Implementation Evaluation of National Pollutant Discharge Standards (Trial) '' (Science and Technology Office 2016 �z 94)
"Administrative Measures for the Automatic Monitoring of Pollution Sources" (Order of the State Environmental Protection Administration No. 28)
"Guiding Opinions on Strengthening the Preparation and Revision of National Pollutant Discharge Standards" (Announcement No. 17 of 2007 of the State Environmental Protection Administration)
"Administrative Measures for the Preparation and Revision of National Environmental Protection Standards" (National Environmental Regulation Science and Technology (2017) No. 1)
The following terms and definitions apply to this standard.
3.1 air pollutants emission standard
In order to prevent environmental pollution, achieve the goal of improving the quality of ambient air, protect human health and the ecological environment, and combine technical and economic conditions and environmental characteristics, limit the types, concentrations, or quantities of atmospheric pollutants discharged into the environment or other factors that cause harm to the environment In accordance with the law, the code of conduct for all kinds of air pollutant discharge activities must be enforced.
3.2 factory boundary
Legal boundaries of industrial enterprises. If the boundary cannot be determined, it refers to the actual boundary.
3.3 fugitive emission
Atmospheric pollutants are not discharged through the exhaust canister, but are discharged into the environment through gaps, vents, and similar openings (holes).
3.4 Existing enterprise existing facility
An industrial enterprise or production facility that has been put into production or that the environmental impact assessment document has passed the review before the date of implementation of the emission standard.
3.5 New facility
Newly constructed, rebuilt and expanded industrial enterprises or production facilities construction projects whose environmental impact assessment documents have passed the review from the date of implementation of the emission standards.
3.6 Special limitation for air pollutants
The air pollutant emission limits formulated and implemented in order to prevent regional air pollution, improve environmental quality, further reduce the emission intensity of air pollution sources, and use more advanced international emission control technologies to control emissions more strictly apply to key regions.
3.7 air pollutants emission standard for industry
Air pollutant emission standards applicable to a particular industry are also called industry-applicable air pollutant emission standards.
3.8 air pollutants emission standard for general facilities
Air pollutant emission standards applicable to general equipment, general operating processes, etc. in multiple industries. General air pollutant emission standards include boilers, electroplating, foundry, industrial furnaces, and malodorous air pollutant emission standards.
3.9 integrated air pollutants emission standard
Air pollutant emission standards applicable to pollution sources in other industries that do not have industrial and general air pollutant emission standards.
4.1 The national air pollutant emission standard system consists of three types of industry-standard, general-purpose and comprehensive emission standards. Industry-level air pollutant emission standards apply to companies in specific industries, and comprehensive air pollutant emission standards apply to companies that do not have industry-level air pollutant emission standards. General air pollutant emission standards apply to all enterprises or production facilities with corresponding emission facilities or pollutant emission behavior.
4.2 Different laws are applicable to the discharge of air pollutants, water pollutants and noise, and the requirements for pollution control of solid waste. In principle, national air pollutant emission standards should be formulated separately.
4.3 When the pollutants discharged from the emission source have the possibility of transferring between water and gaseous media, their emission control requirements can be included in an emission standard. The emission control requirements for air pollutants generated during the solid waste treatment and disposal process belong to the scope of emission standards and can be included in the solid waste pollution control standards.
5.1 Principle of Legitimacy. National air pollutant emission standards should be formulated in accordance with the law. The regulated pollutant discharge behaviors are those permitted by law. The technical requirements stipulated should meet the requirements of national environmental protection laws and other relevant laws and regulations, and meet environmental impact assessment and pollutant discharge. Environmental management system requirements such as permits, sewage charges, environmental protection taxes, and regulatory enforcement.
5.2 Strategic principles. The standard preparation team should have a strategic vision and be able to determine the pollutant emission control requirements in the standard according to national economic and social development plans and plans, environmental protection plans, and national development strategic plans, industrial policies, and access conditions for the industries to which the emission sources belong. The formulated emission standards can promote technological innovation in production processes and industrial restructuring, and optimize economic development.
5.3 The principle of fairness. The standards preparation unit should be environmental protection and public welfare, be able to objectively and impartially investigate and evaluate the production process of the pollution source, the atmospheric pollutant discharge situation, and the level of emission control technology, etc., and truly reflect the emission characteristics of the emission source, and refer to the control of similar foreign emission standards. Standards are formulated based on technical level and opinions from environmental protection, industrial production, and the public to ensure standards are fair and credible.
5.4 Reachability Principle. The production process and emission control technology should be classified and classified, and the compliance technologies and economic costs of various types of emission limits, as well as the compliance technologies or technology combinations of each type of enterprise after the implementation of the standards, make the formulated emission standards technically feasible and economical. Reasonable and operable.
5.5 Coordination principles. The emission standards formulated should be linked to other industry-type, general-purpose or comprehensive air pollutant emission standards to avoid cross-overlaps and be accompanied by applicable environmental monitoring standards.
6.1 Working procedures
6.1.1 In accordance with the requirements of the ��Administrative Measures for the Preparation and Revision of National Environmental Protection Standards�� (National Environmental Regulation Science and Technology No. 2017 �{ 1), the procedures for the preparation and revision of national air pollutant emission standards are divided into opening questions, soliciting opinions, submitting for review, Five stages, including approval, numbering and release.
6.1.2 Demonstration stage. The project undertaking unit establishes a standard preparation team, prepares a title opening demonstration report and a draft of the standard text, conducts a project opening demonstration, and determines the scope of application of the standard, the technical route and work plan for standard preparation.
6.1.3 Solicitation of opinions. The standard preparation team carried out the work according to the work plan determined by the opening report argumentation, and prepared the standard consultation draft and preparation instructions. Technical review of drafts of proposed standards and drafting instructions. After passing the technical review, it will openly solicit opinions from relevant units and the public.
6.1.4 Submission stage. The standard preparation group summed up and handled the feedback opinions, revised and formed the standard submission draft and the review draft preparation instructions, and carried out the technical review of the standard submission draft.
6.1.5 The approval stage. After passing the technical review, according to the opinions of the technical review, a standard report is submitted for drafting and a description is prepared, which is submitted to the administrative department for administrative review, including review by the secretary meeting, ministerial special meeting, and ministry executive meeting.
6.1.6 Numbering and release stage. The management department handles standard approval (number) and release.
6.2 Technical route
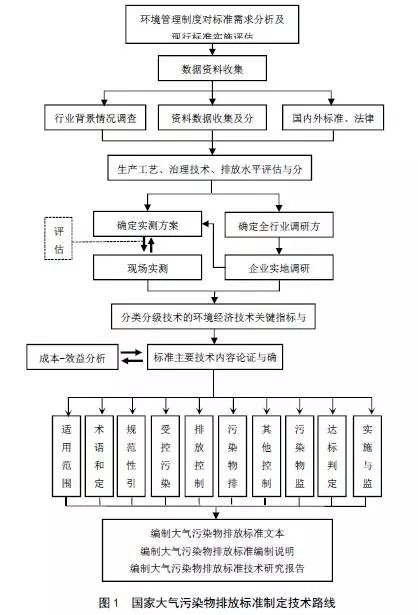
6.2.1 The formulation of national air pollutant emission standards shall carry out management needs analysis, assessment of the current standard implementation, evaluation, data collection, industry research, on-site measurement, standard technical content demonstration, and standard-related material preparation. The technical route is shown in Figure 1.
6.2.2 Analysis of environmental management needs. Analyze national economic development plans and environmental protection plans, industrial development plans and industry access conditions, as well as environmental management requirements such as environmental air quality standards, environmental impact assessments, pollution permits, total volume control, sewage charges or environmental protection tax collection, law enforcement supervision and other environmental management Requirements, summarize and refine the environmental management needs for formulating air pollutant emission standards.
6.2.3 Evaluation of current standards. Based on the analysis of environmental management needs, combined with the conclusions of the existing evaluation of air pollutant emission standards, the focus of standard development or revision is proposed, or in accordance with the "Guidelines for the Implementation of National Pollutant Emission Standards Evaluation Evaluation (Trial)" (Science and Technology Office 2016) No. 94) Analyze and study the problems existing in the current standards, including the applicability of the standards, pollutant control items, emission limits, monitoring requirements, and compliance requirements.
6.2.4 Collection of emission data. Investigate the background of the emission source industry across the country, collect industry emissions data, relevant domestic and foreign emission standards and laws and regulations, production processes, end treatment technologies, and emission control levels.
6.2.5 Field survey of typical enterprises. Based on the background information of the pollution source industry, the analysis identifies representative companies, formulates research plans, and conducts field surveys of selected representative companies to understand the industry's production and emissions characteristics.
6.2.6 Field measurement of typical enterprises. In-depth analysis of on-site survey results of typical enterprises, formulate actual measurement plans for enterprises that really need on-site measurement, carry out systematic and comprehensive on-site measurement, and grasp the characteristics of atmospheric pollutant emissions.
6.2.7 Evaluation of classified emission control technology. Comprehensively analyze the collected emission data, field survey results and field measurement results, list the emission control technology list and corresponding technical parameters, evaluate and classify the emission control technology.
6.2.8 Standard technical content is determined. Comprehensive environmental management needs analysis results, current emission standard implementation evaluation results, various related data analysis and measured data analysis results, emission control technology classification and evaluation results, determine the scope of application of standards, pollutant control items, emission control indicators, emission limits Value, monitoring requirements, standards and other requirements.
6.2.9 Preparation of standard-related materials. Including the preparation of standard texts, preparation of instructions and technical reports.
7.1 Standard structure
The structure of national air pollutant emission standards mainly includes the cover, table of contents, preface, standard name, scope of application, normative reference documents, terms and definitions, requirements for pollutant emission control, monitoring requirements, compliance requirements, implementation and supervision.
7.2 Cover and Table of Contents
Follow the regulations in HJ 565
7.3 Foreword
7.3.1 In the foreword, the legal basis and purpose of the standard shall be clearly defined, and the main content of the standard shall be briefly described. If it is a revised standard, it shall briefly describe the previous versions of the standard revision, the main content of this revision, and the substitution relationship with other standards.
7.3.2 The foreword of the industry-type air pollutant emission standards shall clearly specify that the corresponding national pollutant emission standards shall be applicable to the discharge of malodorous pollutants, water pollutants and environmental noise by enterprises, and the identification, treatment and disposal of solid waste shall be applicable to national solid waste pollution. Control standards.
7.3.3 It should be clear that local provincial-level people's governments can formulate local air pollutant emission standards for items not specified in the standard; for items that have been specified in the standard, local air pollutant emission standards that are stricter than that standard can be formulated. When the requirements of an environmental impact assessment document or a pollution discharge permit are stricter than the standards or local standards, the approved environmental impact assessment or pollution discharge permit document shall be implemented.
7.3.4 The time for the current and new enterprises to implement the standards shall be specified, as well as the time for the standard setting unit, drafting unit, approval and release implementation.
7.4 Application
7.4.1 The main technical content and application of the standard should be accurately defined, and the non-applicability of the standard, and the implementation of other standards by relevant production units (processes) and the implementation of other production units (processes) with reference to this standard should be clearly identified when necessary. .
7.4.2 It should be clear that the national air pollutant emission standards are only applicable to pollutant emission behaviors permitted by law. For emission behaviors prohibited by law, the emission standards do not stipulate emission control requirements.
7.5 Normative references
7.5.1 Clarify national environmental protection standards, other national standards, or international standards, etc., as cited in the standard text. Do not cite standards that have been abolished by the state.
7.5.2 The order of cited documents shall be implemented in accordance with the provisions of HJ 565, and the introduction shall comply with the requirements of Appendix 12 of the ��Administrative Measures for the Preparation and Revision of National Environmental Protection Standards��.
7.6 Terms and definitions
7.6.1 The terms and definitions necessary for understanding the standard shall be given in the order in which they appear in the standard text.
7.6.2 Terminology and definitions should try to adopt the definitions in national environmental protection standards, other national standards or international standards, and have accurate sources. If there are no reference terms and definitions, scientific, accurate and concise terms and definitions should be determined on the basis of sufficient literature research and in-depth demonstration.
7.7 Pollutant emission control requirements
7.7.1 Pollutant emission control requirements shall include the time for existing and new enterprises to implement standards, pollutant items, control indicators, emission limits, monitoring locations, and requirements for fugitive emission control. Emission standards may also specify technical and management measures to implement the standards.
7.7.2 In general, existing enterprises should meet the emission control requirements of newly-built enterprises with a transition period of 1-3 years. New enterprises should implement after the release of emission standards. The geographical scope and time for implementing the special emission limit of air pollutants shall be prescribed by the competent department of environmental protection under the State Council or the provincial people's government.
7.7.3 Emission limits include organized emission limits and fugitive emission limits, which are usually listed in a table. Organized emission limits are proposed for each emission node that can be emitted through the exhaust pipe, and special emission limits should also be proposed for key areas. Propose fugitive emission limits for typical fugitive emission nodes within the plant boundary and within the enterprise.
7.7.4 The monitoring position corresponding to each pollutant emission limit shall be specified in the standard. For emission nodes that cannot establish emission limit values, technical requirements for emission control and emission management should be proposed for the production process.
7.7.5 In order to prevent dilution and discharge, the standard shall also provide the standard exhaust volume, oxygen content, excess air coefficient or air mixing coefficient per unit product. The standard should set out the basic requirements for the height of the exhaust cylinder, and the specific height requirements should be determined through environmental impact assessment.
7.8 Pollutant monitoring requirements
7.8.1 The emission standards should include enterprise self-monitoring, discharge port setting, sample collection, and analysis method requirements, so that the proposed pollutant emission control requirements can be verified and confirmed through technical or management means.
7.8.2 In the emission standards, enterprises should be required to establish an enterprise monitoring system and formulate a monitoring plan in accordance with the requirements of the Environmental Monitoring Management Measures and other regulations, to conduct self-monitoring of the atmospheric pollutant discharge status and its impact on the surrounding environment quality, and to preserve the original Monitor records and publish monitoring results.
7.8.3 For the setting of discharge outlets, enterprises shall be required in the standard to design, construct and maintain permanent sampling outlets, sampling test platforms and sewage outlet signs in accordance with the requirements of environmental monitoring management regulations and technical specifications.
7.8.4 The requirements for the installation of automatic monitoring equipment for key pollution sources (including facilities, installations, etc.) should be put forward in the standard, and implemented in accordance with the relevant laws and the ��Measures for the Automatic Monitoring and Control of Pollution Sources��.
7.8.5 For the frequency and sampling time of air pollutant emission monitoring, the standards shall be implemented in accordance with the relevant national technical specifications for environmental monitoring. For special requirements, the frequency and sampling time of monitoring should be specified in the standard.
7.8.6 The sampling point setting and sampling method shall be implemented in accordance with the standards of GB / T 16157 and HJ 397. For fugitive emissions, sampling and monitoring shall be performed in accordance with the standards of HJ / T 55 and other standards. The determination of air pollutant concentrations shall adopt the national environmental monitoring and analysis method standards, and the standards cited shall be listed in the standards.
7.8.7 For the verification of enterprise product output, it shall be stipulated in the standard that it is based on statutory statements.
7.9 Determination of compliance
7.9.1 Standards for manual monitoring of pollutants shall be specified in the standard. If the monitoring result obtained in accordance with the relevant manual monitoring technical specifications exceeds the emission concentration limit, it is determined that the emission exceeds the standard.
7.9.2 The standards shall be specified in the standards for the determination of compliance with online (automatic) monitoring of pollutants. Within a certain period of time (such as 24 hours, months, years, etc.), the average pollutant emission level exceeds the discharge limit a certain number of times or multiples.
7.10 Implementation and supervision of standards
Standards should provide basic implementation and supervision requirements, including the subject and content of implementation and supervision. The main body for the implementation and supervision of national air pollutant emission standards is usually the environmental protection administrative department of the people's government at or above the county level.
8.1 Data Collection and Analysis
8.1.1 Collect the latest relevant environmental protection laws and regulations, national economic development plans, national environmental protection plans, industry development plans, industrial development strategic plans, industry access conditions, and other relevant laws, regulations, and policy documents, and analyze the country's latest Environmental management requirements and industry and industry development strategies.
8.1.2 The production data of the surveyed industries mainly include: the number of enterprises in the country and other countries in the world, regional distribution, size, types of production processes, number of production equipment, and recent years' output, output value, and proportion of the total national output value, and Clean production process application, raw material and fuel consumption, industry development history, etc., analyze industry production characteristics, future mainstream production processes and future development trends.
8.1.3 Survey of industry emissions data, mainly including: chemical composition of production raw materials, production levels of pollutants, emission levels, industry-wide emissions and the proportion of total national emissions, environmental impacts of pollutant emissions, and emission control technologies And investment costs, operation and maintenance costs and their proportions, and environmental management measures. Analyze the development trend of future emission control technologies.
8.1.4 Collect enterprise emission data, mainly including: online monitoring, supervisory monitoring, manual monitoring by the enterprise, environmental protection acceptance monitoring data of construction project completion, including hourly and daily average emission concentration of pollutants, exhaust volume, oxygen content and Enterprise design output, actual output, production load, etc. Analyze pollutant discharge levels, compliance standards, and discharge characteristics of various production processes.
8.1.5 Collect relevant emission standard data, mainly including: the United States, European Union, Japan, Germany and other major countries, regions and relevant international organizations' emission standards, China's relevant industry pollutant emission standards. Analyze the existing scope of China's current emission standards, the scope of emission control requirements, and monitoring requirements.
8.2 Enterprise Site Investigation
8.2.1 According to factors such as production process types, raw material types, products, scales, emission control technologies, control levels, and national distribution adopted by existing enterprises, select nationally representative and advanced emission control companies to conduct on-site Research. Conduct in-depth analysis of the production and emission data of the companies to be investigated, and formulate a reasonable and feasible field investigation plan.
8.2.2 In-depth study of selected representative enterprise sites to investigate the company's production raw materials and components, fuel types and sources, process and cleanliness, organized and unorganized emission nodes, types of pollutants, emission control technology levels, and emission control devices Investment cost, operating cost, annual output value and profit of the enterprise. Communicate with the technical staff of the enterprise about the problems existing in the implementation of the current standards, the improvement of production processes and the potential of emission control technologies.
8.3 Typical enterprise measurement
8.3.1 During the data collection and on-site investigation phase, the measured data collected should be able to cover the representative device types of more than 80% of the industry's production capacity, cover all device types covered by the applicable scope of the standard, and reflect the industry's air pollutant emission characteristics. The necessary data for the establishment of emission limits are available; otherwise, actual measurements should be arranged for typical enterprises.
8.3.2 A scientific and reasonable practical measurement plan shall be formulated according to the production and emission characteristics of the emission source. Before the actual measurement, experts must be organized to confirm the measurement plan. Analyze and evaluate the preliminary test results, and if necessary, adjust the actual measurement plan in time to ensure that the data is detailed and credible, ensure the integrity of the data at each key link, and reflect the characteristics of pollutant emissions.
8.4 Environmental economic and technological key indicators and parameters of classification and classification technology
8.4.1 Based on the obtained emission control technology data, list the emission control technology for each pollutant and the technical principles of each emission control technology, analyze the essence of each emission control technology principle, and the advantages and disadvantages of the emission control technology. Classification of emission control technologies. For cleaner production technologies, they should be classified separately.
8.4.2 Through analysis of field investigation data, online data, and field measured data related to each emission control technology, determine the removal efficiency, emission level, fixed investment cost, operating cost per unit of pollutant removal, etc. of each emission control technology, etc. Key indicators and parameters of environmental economic technology, as well as other environmental impacts, environmental benefits, and economic benefits.
8.4.3 Classify each type of emission control technology according to the above technical index parameters. Based on the international advanced control technology level, determine the technology or technology combination of different emission control levels with industry applicability.
8.5 Determination of scope of application
8.5.1 Based on the collected data on the production and discharge of various pollutants, analyze the types of production processes, scale of production equipment, types and sources of raw materials, product types and destinations, and the requirements for the elimination of production processes by national industry access policies, etc. All sources that can be involved. Analyze the applicable scope of the current emission standard or the existing enterprise's applicable emission standard, evaluate the control scope that the proposed emission standard can achieve, and accurately define the applicable scope of the proposed emission standard.
8.5.2 When determining the applicable scope, it shall be effectively connected with other relevant emission standards. For enterprises or production units that are applicable to industry-level air pollutant emission standards, the general-purpose equipment or the general operating processes thereof still apply the general air pollutant emission standards. For enterprises or pollution sources that are not controlled by applicable industry-type air pollutant emission standards and general air pollutant emission standards, comprehensive air emission standards apply.
8.5.3 For malodorous pollutants, GB 14554 is still implemented in principle. If it is an odorous pollutant outside the scope of GB 14554, it should be controlled in the proposed emission standard. If the pollutants controlled in GB 14554 are discharged, but they are characteristic pollutants that need to be further strictly controlled, the control requirements may be specified in the draft emission standards, except for the odor concentration.
8.6 Determination of emission control requirements
8.6.1 Pollutant emission control requirements include pollutant control items, control indicators, organized emission limits, fugitive emission limits, baseline exhaust volume, baseline oxygen content, baseline excess air coefficient or air mixing coefficient, and exhaust cylinders High requirements and technical and management requirements for organized and unorganized emissions control. Emission control requirements should be able to be verified and confirmed through technical or management means.
8.6.2 Based on the collected data and actual measurement results, a comprehensive pollutant inventory is developed, the emissions of each pollutant are calculated, the degree of pollution hazards, the maturity and economic affordability of pollution control technologies, and pollutant sampling are evaluated. Analyze the suitability of analysis methods, analyze the correlation between pollutants, etc., and consider the above factors to determine the pollutant control project.
8.6.3 When determining pollutant control projects, all pollutants (particulate matter, volatile organic compounds, etc.) that have a significant impact on public health and the ecological environment when the total amount of pollutants (sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides) are controlled, and the national key prevention and control Heavy metal pollutants (lead, cadmium, chromium, mercury, arsenic, etc.), international compliance pollutants (dioxins, etc.), pollutants in the Priority Control Chemical List, and other harmful pollutants and characteristic pollutants should be focused consider.
8.6.4 The pollutant emission control indicators shall be reasonably determined in accordance with the requirements of environmental impact assessment, pollution permits, sewage charges, law enforcement supervision, and other institutional requirements, the characteristics of pollution source emissions, and the feasibility of monitoring. The types of pollutant emission control indicators generally include mass concentration indicators (such as mg / m3), emission rate indicators (such as kg / h), performance indicators (input: kg / t raw materials; output: kg / t products, etc.), pollutant removal Rate index (% removal) and so on.
8.6.5 The emission limits of conventional pollutants (particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, etc.) should be set for different pollution sources and according to the corresponding control technology. For new enterprises, strict emission limit requirements should be set in accordance with internationally advanced best available technologies; for existing enterprises, it should be stipulated that the limit requirements for new enterprises should be reached within a certain period of time; for special emission limits, international leading controls Technical or environmental quality standards set the most stringent emission control requirements.
8.6.6 The emission limit of toxic and harmful pollutants shall be based on the requirements for protecting human health, and adopt the methods, actual measurement results, emission control technology levels and methods in the "Principles and Methods for Establishing Local Air Pollutant Emission Standards" (HJ ������). Emission limits in relevant standards at home and abroad, as well as occupational exposure limits for harmful factors in the workplace, acceptable levels of health risks, and other factors have been comprehensively considered and determined.
8.6.7 The boundary concentration limit of air pollutants shall be determined according to the requirements for protecting human health, and shall be determined based on factors such as ambient air quality standards, occupational exposure limits for harmful factors in the workplace, and acceptable levels of health risks. If the emission limit of the unorganized emission point in the plant area is established, it shall be determined based on the actual measurement results and control technology. The formulated emission limit requirements should be able to promote enterprises to transform unorganized emissions into organized emissions for control. The enterprise shall reach the plant boundary concentration limit.
8.6.8 When formulating pollutant emission control technology and management requirements, the production process and the characteristics of pollutant emissions should be studied in depth. Under the premise of not affecting production safety, specific recommendations for production processes, pollution control equipment, etc. Control requirements for operating technical parameters and requirements for daily environmental management.
8.6.9 On the basis of a comprehensive survey of existing enterprises across the country, and in combination with the production process design requirements of typical enterprises, the baseline exhaust volume, baseline oxygen content, baseline excess air coefficient, or air mix coefficient should be reasonably determined.
8.6.10 When formulating emission control requirements, a clear technical route or technical combination (for example, clean production + end-of-line governance) shall be given to various types of enterprises nationwide based on the identified classification and grading technology. Each pollutant emission limit set in the standard should have a corresponding technology that meets the standards, and there are actual application cases and stable operation.
8.6.11 In the preparation of the description and research report, the technical name, technical route, technical level, key parameters, economic costs, environmental benefits, etc. of the technologies that meet the standards shall be specified. If there is no feasible technology for achieving the standard, it shall be evaluated and proposed in accordance with the requirements of HJ ������ (Guidelines for the Preparation of a Guide to a Feasible Technology).
9.1 Basic requirements
9.1.1 Where reference to existing monitoring method standards can meet emission monitoring requirements, monitoring method standards should be cited. If there are special monitoring requirements for pollution sources, they should be verified and demonstrated through experiments and clearly specified in the emission standards. The monitoring methods cited shall prove to be suitable for monitoring such sources.
9.1.2 When citing the monitoring method standard, an in-depth analysis should be made to determine whether the target pollutants specified in the standard are consistent with the pollutant items in the emission standard, whether the technical parameters such as detection limit and lower detection limit can meet the requirements of the emission limit and the method standard Implementation, clearly prioritizing the selection criteria, and when each monitoring method is applicable or not.
9.1.3 If there is no national environmental monitoring and analysis method standard available for the air pollutants to be controlled in the emission standard, it shall report to the standard-setting authority, propose proposals in a timely manner, and request that the monitoring and analysis method standard be developed as soon as possible to ensure the release of the emission standard At the time, all pollutant control projects had applicable monitoring and analytical method standards.
9.2 Selection principles
9.2.1 National environmental monitoring method standards are preferred for pollutant discharge monitoring. For pollutants that have no national environmental monitoring method standards, their limits will be implemented after the national environmental monitoring method standards are issued.
9.2.2 The national environmental monitoring and analysis method standard shall meet the basic requirements of HJ 168, and its lower limit of measurement shall not be lower than the requirements for accurate and quantitative determination of pollutant control projects, and the precision and accuracy shall not be lower than the corresponding general method requirements.
10.1 Analysis of the distribution of pollution emission concentration
10.1.1 Collect data such as online monitoring, supervision and enforcement, and enterprise self-monitoring, and analyze the hourly average concentration, daily average concentration, weekly average, monthly average concentration, and seasonal average of air pollutants on the basis of deducting emissions data under abnormal operating conditions. Statistical distribution of concentration.
10.1.2 According to the statistical distribution rule, analyze the statistical relationship between the average concentrations in different periods, and establish the statistical requirements for meeting the standards between daily average weekly average, monthly average, quarterly average, annual average concentration limit, and hourly average concentration limit. , Or meet the statistical requirements for compliance between the monthly, seasonal, and annual average concentration limits and the daily and hourly average concentration limits.
10.2 Requirement determination
10.2.1 According to the analysis of the statistical requirements for compliance with standards and China's emission management requirements, combined with the standards for determining compliance with key industrial source emission standards in developed countries and regions such as the United States, Germany, and the European Union, an atmosphere capable of meeting on-site law enforcement and routine supervision is proposed. The requirements for the determination of pollutant discharge standards, that is, the number of times or multiples of exceeding the allowable limit of the average time emission limit.
10.2.2 If the actual exhaust gas volume or oxygen content or excess air coefficient of a unit product exceeds the benchmark exhaust gas volume or baseline oxygen content or baseline excess air coefficient of a unit product, the measured atmospheric pollutant concentration shall be converted into the atmospheric pollutant baseline exhaust gas Emission concentration or reference oxygen content or reference excess air coefficient emission concentration, and use this concentration as the basis for judging whether the emission meets the standard. The statistical cycle of product output and exhaust volume is one working day. For conversion of air pollutant reference emission concentration, refer to formulas (1) to (3).


11.1 Prediction of pollutant emission reduction and environmental quality improvement effects
11.1.1 Based on the requirements of industrial policies, industry access, environmental policies, etc., analyze the development trend of the applicable industry for the standards in the country for 5-10 years, mainly including the annual growth rate of various production process devices, and product output trends And pollution prevention technology and energy structure adjustment.
11.1.2 When forecasting the effect of emission reduction, first analyze the national annual emissions of each pollutant when the current standards are implemented for existing enterprises, new enterprises in the next 5-10 years and all enterprises based on the trend of product output, and then analyze the existing Annual emissions of various pollutants by enterprises, new enterprises in the next 5-10 years and all enterprises when the new standards are reached. Calculate emissions reductions and reduction ratios for each year in the future based on emissions from current and new standards.
11.1.3 For industries with large emissions of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds, the improvement of ambient air quality by the implementation of standards should be predicted. It should be based on the premise that the pollutant emission limit stipulated in the air pollutant emission standards meets the standards, and in combination with the industry development plan, design different scenarios for the industry scale, pollution prevention technology, energy structure, and whether the standards are fully implemented in the next 5-10 years. Reductions in emissions, predicting the contribution of air pollutant emission standards to the improvement of ambient air quality.
11.2 Economic Costs and Benefits Analysis
11.2.1 Based on the classification and grading technology, the existing enterprises and newly-established enterprises will meet the technical standards for pollutant emission standards, and determine the applicable emission control technology or technology combination for various types of enterprises. Based on the collected investment data and operating data of each type of emission control technology, the fixed investment cost and annual operating cost of each typical emission control device were determined through analysis.
11.2.2 According to the collection of the existing production equipment, emission control device distribution and pollutant emission levels of existing enterprises across the country, determine the number of new and newly added emission control devices that existing enterprises need to transform. Based on the fixed investment costs and annual operating costs of each set of typical emission control devices, calculate the fixed investment and operating costs that companies in the industry need to increase, as well as the increase in fixed investment and the increase in annual production and operating costs.
11.2.3 For the implementation of new emission standards, promoting the popularization of clean production processes in the industry, reducing material consumption, energy consumption, and increasing product output, the economic benefits of the implementation of the standards should be analyzed, including the number of cleaner production process devices and costs increased by enterprises in the industry , The economic benefits of enterprises across the industry as a result of reducing material consumption, energy consumption, and increasing product output, as well as net costs or costs after deducting economic benefits.
The main contents of the standard preparation instructions include project background, industry overview, analysis of the necessity of standard development, analysis of industrial production and pollution and pollution control technology, analysis of environmental impacts of toxic and harmful pollutants emitted by the industry, main technical content of standards, and major countries and regions Research on relevant standards of international organizations, environmental benefits and economic and technical analysis of standards implementation, comments on standards, technical review and administrative review.
The standard technical report shall elaborate the key technical content and main technical basis of the standard formulation in the form of text, diagrams, etc. based on the preparation of the description. The standard technical report shall be prepared in synchronization with the preparation instructions and shall be prepared in accordance with the format requirements of scientific research literature.
Appendix A
(Informative appendix)
Content and format requirements for the opening and demonstrating report of national air pollutant emission standards
A.1 Project background
A.1.1 Task source
The year when the Ministry of Environmental Protection issues the project, the document number, and the project's unified number, and the full name of the unit that undertakes and revises the standard project.
A.1.2 Working process
Relevant investigation and research work carried out by the project undertaker after the task is issued.
A.2 Basic situation of drafting and revising standards
A.2.1 The main content of the standard
Including scope of application, requirements for pollutant emission control, requirements for pollutant monitoring, implementation and supervision.
A.2.2 Legal status and role of standards
The legal status of the standard, its status in the national environmental standard system, its relationship with other emission standards, and its role after implementation.
A.3 Relevant situation and development trends at home and abroad
A.3.1 Industry Overview
(1) The status of the industry scale, including production capacity and annual output, annual total output value (proportion of the national total annual industrial output value), the number of enterprises, and the scale of enterprises.
(2) Geographical distribution of enterprises in the industry, in the form of tables and diagrams, explain the distribution of enterprises in various provinces, watersheds and regions.
(3) The status of major products in the industry.
(4) Industry product market supply, import and export status (China's share of world output, etc.).
(5) Forecast of industry development trends.
(6) Other issues that need explanation.
A.3.2 Situation of the industry abroad
(1) The number and geographical distribution of enterprises in the industry (US, EU, Japan and other countries and regions).
(2) Annual output and production capacity of major products in the industry.
(3) Market supply, import and export of industrial products.
(4) Forecast of industry development trends.
(5) Other issues that need explanation.
A.4 Sewage discharge from industry
A.4.1 Analysis of main production processes and pollution generation in the industry
(1) Production raw materials, technical routes and production processes adopted by the industry.
(2) Pollution producing nodes and exhaust emission methods in the production process.
(3) Types of discharged pollutants, including pollutants with large emissions, toxic and hazardous substances with industry characteristics, such as heavy metals, toxic organics, environmental hormones, persistent organics, etc.
(4) Analysis of the amount of pollutants generated by the industry.
(5) Other issues that need explanation.
A.4.2 Current status of industry emissions
(1) Enterprise survey data sheet (covering various scales, various places and various production processes).
(2) Analysis of industry's pollution level.
(3) The total annual emissions of pollutants from the industry, and the proportion of the total national emissions.
(4) The annual emissions of major air pollutants in the industry and the proportion of the total national emissions, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, volatile organic compounds and mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, lead, arsenic, etc.
(5) Other issues that need explanation.
A.5 Necessity analysis of standard system (revision)
A.5.1 Relevant requirements of the state and environmental protection authorities
(1) The state's latest requirements for environmental protection and the industry.
(2) Requirements for the industry in the five-year plan for national economic and social development.
(3) Requirements related to the industry in the five-year national environmental protection plan.
(4) Requirements for the industry in other relevant documents of the environmental protection department
A.5.2 Environmental protection requirements in relevant national industrial policies and industry development plans
(1) Industry development planning.
(2) Industry policy.
(3) Industry access policies.
A.5.3 Major environmental issues brought by industry development
(1) What are the main pollutants produced at each stage of the production process?
(2) The amount of major pollutants discharged, and the proportion of the total pollutant emissions in the country.
(3) Related pollution accidents, environmental lawsuits, etc.
A.5.4 Latest developments in industry clean production processes and pollution prevention technologies
(1) The latest progress of clean production technology and pollution control technology.
(2) Guidance documents for the state to implement relevant advanced technologies.
A.5.5 Main problems in current environmental protection standards
(1) The name and number of the current environmental protection standards implemented by this industry.
(2) Analyze whether the types of pollutants controlled in the current environmental protection standards are comprehensive.
(3) Analyze whether the pollution control indicators set in the current environmental protection standards are reasonable.
(4) Analyze whether the emission limit of pollutants in the current environmental protection standards can meet the requirements of current environmental protection work.
(5) Analyze whether the current environmental protection standards meet the current thoughts and requirements of environmental protection standards.
(6) Other issues that need explanation.
A.6 Status of relevant emission standards at home and abroad
(1) United States
(2) European Union
(3) Japan
(4) International organizations (such as World Health Organization, World Bank, etc.)
(5) Other countries and regions
A.7 Principles, methods and technical routes to be adopted in the development of standards
A.7.1 Principles to be adopted
Refer to "Guiding Opinions on Strengthening the Preparation and Revision of National Pollutant Discharge Standards" (formerly the State Environmental Protection Administration Announcement No. 17 of 2007) and "Administrative Measures for the Preparation and Revision of National Environmental Protection Standards" (National Environmental Regulation Science and Technology (2017) No. 1) Wait.
A.7.2 Proposed method
Mainly describe the methods used, such as literature research, field research, public participation, expert discussions, etc.
A.7.3 Proposed technical route
Mainly describes the technical process of making (repairing) this standard.
A.8 Main work to be carried out
A.8.1 Related research work
It mainly includes the status quo of the industry at home and abroad, analysis of process nodes for pollutant generation, characteristics and analysis of pollutant discharge, status and analysis of pollution control technology, impact of pollutants on the environment, and relevant standards at home and abroad.
A.8.2 Terms and definitions
Clearly define the industry scope, technology, products and other terms of this standard that are closely related to the scope of application of this standard.
A.8.3 Determination of scope of application
Determine the scope of application of this standard, the circumstances in which it does not apply, and the relationship between this standard and other relevant standards.
A.8.4 Determination of pollutant items
The conventional pollutants and characteristic pollutants that need to be controlled by this standard are determined according to the industry's pollutant generation, the impact on human health and the ecological environment, and the national total control pollutants.
A.8.5 Determination of emission limits
Determine the concentration limit of each pollutant according to industrial development, pollutant generation characteristics, relevant domestic and foreign standards, pollutant concentration limit, pollution control technology level and cost.
A.8.6 Division of the implementation period of this standard
Analyze the time requirements for the implementation of this standard by new and existing enterprises based on analysis of relevant information such as industry profiles and pollution control technologies.
A.8.7 Requirements for pollutant monitoring and supervision
The monitoring position, monitoring method, and implementation supervision requirements of each pollutant controlled in the standard determine the standards of the monitoring methods to be referenced.
A.8.8 Major issues for discussion
A.9 Main results to be submitted
(1) Solicitation stage: Standard draft for soliciting opinions, preparation of instructions and technical report.
(2) Submitting stage: Standard submitting manuscript and preparing instructions and technical report.
(3) Approval stage: Approval of standard report and preparation of instructions and technical report.
A.10 Basic conditions for the project undertaker's work related to the formulation and revision of standards
Previous standards development and revision work, standards research work experience, awards.
A.11 Cooperative units and task division
A.12 Fund utilization plan and personnel input
A.12.1 Fund utilization plan
State the expected expenditure direction and amount of funds in a table.
A.12.2 Staff input
Describe in tabular form the personnel who participated in the standard revision project.
A.13 Time schedule
According to the time when the tasks are issued and the requirements of the ��Administrative Measures for the Preparation and Revision of National Environmental Protection Standards,�� standard work schedules are proposed to clarify the timing of completion of each task.
Appendix B
(Informative appendix)
Content and format requirements for the preparation of national air pollutant emission standards
B.1 Project background
B.1.1 Mission source
(1) The standard (repaired) items are included in the annual plan of the Ministry of Environmental Protection and the document number of the issued plan.
(2) The full name of the undertaking unit and participating unit of the standard system (repair) project.
B.1.2 Working process
(1) Relevant investigation and research work carried out by the standard preparation group after the task is issued (brief description).
(2) The situation of standard opening discussions.
B.2 Industry Overview
B.2.1 Overview of the development of the industry in China
(1) Industry scale status, including production capacity and annual output, annual total output value (proportion of the national total annual industrial output value), enterprises
Quantity, enterprise size, etc.
(2) Geographical distribution of enterprises in the industry, in the form of tables and diagrams, explain the distribution of enterprises in various provinces, watersheds and regions.
(3) The status of major products in the industry.
(4) Industry product market supply, import and export status (China's share of world output, etc.).
(5) Forecast of industry development trends.
(6) Other issues that need explanation.
B.2.2 Overview of industry development in other countries and regions
(1) The number and geographical distribution of enterprises in the industry (US, EU, Japan and other countries and regions).
(2) Annual output and production capacity of major products in the industry.
(3) Market supply, import and export of industrial products.
(4) Forecast of industry development trends.
(5) Other issues that need explanation.
B.3 Necessity analysis of standard system (revision)
B.3.1 Relevant requirements of the state and environmental protection authorities
(1) The state's latest requirements for environmental protection and the industry.
(2) Requirements for the industry in the five-year plan for national economic and social development.
(3) Requirements related to the industry in the five-year national environmental protection plan.
(4) The requirements of this industry in other relevant documents of the environmental protection department.
B.3.2 Environmental protection requirements in relevant national industrial policies and industry development plans
(1) Industry development planning.
(2) Industry policy.
(3) Industry access policies.
B.3.3 Major environmental issues brought by industry development
(1) Sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, volatile organic compounds, major (characteristic) pollutants, and exhaust emissions in this industry.
(2) The proportion of the main pollutant discharge in this industry to the total pollutant discharge in the country (expressed in the form of charts, tables, etc.).
(3) Related pollution accidents, environmental lawsuits, etc.
B.3.4 Latest progress of cleaner production processes and pollution prevention technologies in the industry
(1) The latest progress of clean production technology and pollution control technology.
(2) Guidance documents for the state to implement relevant advanced technologies.
B.3.5 Main problems in current environmental protection standards
(1) The name and number of the current environmental protection standards implemented by this industry.
(2) Analyze whether the types of pollutants controlled in the current environmental protection standards are comprehensive.
(3) Analyze whether the pollution control indicators set in the current environmental protection standards are reasonable.
(4) Analyze whether the emission limit of pollutants in the current environmental protection standards can meet the requirements of current environmental protection work.
(5) Analyze whether the current environmental protection standards meet the current thoughts and requirements of environmental protection standards.
(6) Other issues that need explanation.
B.4 Industry Pollution and Pollution Control and Analysis of Pollution Control Technology
B.4.1 Analysis of main production processes and pollution generation of the industry
(1) Production raw materials, technical routes and production processes adopted by the industry.
(2) Pollution-producing nodes and emission methods (organized emissions, unorganized emissions) in the production process.
(3) Types of discharged pollutants, including pollutants with large emissions, and toxic and hazardous substances with industry characteristics, such as heavy metals, toxic organics, environmental hormones, and persistent organics.
(4) Analysis of the amount of pollutants generated by the industry.
(5) Other issues that need explanation.
B.4.2 Current status of industry emissions
(1) Enterprise survey data sheet (covering various scales, various places and various production processes).
(2) Analysis of industry's pollution level.
(3) The total annual emissions of industrial waste gas, and its proportion in the total national emissions.
(4) The annual emissions of major air pollutants in the industry and the proportion of total national emissions, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, etc.
(5) Other issues that need explanation.
B.4.3 Analysis of pollution prevention technology
(1) Industry clean production technology.
(2) Industry pollution end treatment technology.
(3) The current situation of air pollution control in the industry (main types of treatment technologies and the proportion of investment in pollution treatment facilities in the total investment, the proportion of the operating costs of treatment facilities in the total cost, etc.).
(4) Propose feasible technologies that meet the requirements for the control of various types of pollutant emissions.
(5) Engineering examples.
B.5 Environmental impact analysis of toxic and harmful pollutants emitted by the industry
Toxic and harmful pollutants include: persistent organic substances, substances on the list of highly toxic chemicals, and other substances that have been proven to cause a "three effects" effect on the human body or cause environmental harm to the ecology.
(1) Chemical name, common name, molecular formula and structural formula of pollutants.
(2) General physical and chemical properties of pollutants.
(3) Toxicological toxicity data of pollutants.
(4) Related pollution accidents and environmental lawsuits.
(5) Recognized environmentally safe concentration (amount).
B.6 Main technical contents of the standard
B.6.1 Application of Standards
(1) Describe the scope and basis of this standard.
(2) Explain the circumstances and basis on which this standard does not apply.
(3) Describe the connection between this standard and other standards.
B.6.2 Standard structural framework
(1) The main chapters included in the standard text.
(2) The time points for the division of existing and newly-built enterprises, and the time (including special emission limits) to implement the standards
(3) The standard divides different production processes and different product types in the applicable industry and the basis of division.
B.6.3 Terms and definitions
(1) List the terms and definitions used in this standard and compare it with the current standard.
(2) Indicate the source of terms and definitions, such as those given in references and compilation groups.
(3) In the narrative process, the content of the standard text should not be copied directly to avoid repetition.
B.6.4 Selection of pollutant projects
(1) Comprehensively analyze and list the main pollutants that may be generated by this industry (it needs to be comprehensively covered, and there can be no major omissions).
(2) Analyze the air pollution control items in the standard one by one, and explain the main basis for selecting and determining the control items, such as total amount control, pollution reduction, ecological and health impacts, and solving regional environmental problems. Relevance between physical items.
B.6.5 Determination and establishment of pollutant emission limits
(1) A detailed analysis and demonstration of the basis for setting each limit item by item.
(2) A detailed analysis and demonstration of each standard's compliance technology is carried out item by item. Existing and newly-established enterprises adopting the technology for achieving standards; technology for achieving special emission limits for air pollutants; applying advanced production processes and clean production technologies.
(3) Comparative analysis with relevant standards at home and abroad, and comparative analysis with the comprehensive emission standards of air pollutants or the current industry emission standards, and a comparison chart is given.
B.6.6 Determination and basis for other pollution control indicators
(1) The basis for determining the reference exhaust volume, reference oxygen content, excess air coefficient or air mixing coefficient per unit of product (survey, statistics, pollution factor, etc.).
(2) Control the fugitive emission limits of gas pollutants and control measures (such as the limits of pollutant concentrations at the border or outside the facility, requirements for collecting and purifying pollutants, etc.), determine the basis for the limits and control measures.
B.6.7 Monitoring requirements
(1) Explain the applicability of the monitoring methods selected in the standard.
(2) Explain the special monitoring requirements in the standard.
B.6.8 Determination of compliance
(1) Explain in detail the basis for determining the compliance requirements of the manual monitoring method.
(2) Describe in detail the determination basis of the online (automatic) monitoring method corresponding to the determination of compliance with the standard.
B.7 Research on relevant standards of major countries, regions and international organizations
B.7.1 Relevant standards of major countries, regions and international organizations
(1) Control history (development of the industry in the country, successful experiences and lessons learned from pollution control)
(2) Pollution control measures
(3) Relevant laws and regulations
(4) Control technology (best available technology, etc.)
(5) Relevant standards (need to indicate the age of foreign standards)
B.7.2 Comparison between this standard and similar standards of major national, regional and international organizations
(1) The comparison of pollutant emission limits and pollution control levels of this standard with other countries can be quantified or qualitatively stated. Attention should be paid to the time when the foreign standards were formulated and the development of the industry in that country.
(2) Use chart and table.
(3) Elucidate the conclusion of comparison.
B.8 Environmental benefits and economic and technical analysis of the implementation of this standard
B.8.1 Environmental (emission reduction) benefits of implementing this standard
(1) Analysis of pollutant emission reduction of existing enterprises under the current standards and after the implementation of this standard.
(2) Existing enterprises' total pollutant emissions that can be reduced by the limits of this standard (stocks, tons / year).
(3) Prediction and analysis of pollutant emissions of new enterprises after implementing this standard.
Principles and methods for setting local air pollutant emission standards
Principlesandmethodsforthedevelopmentof
Localemissionstandardsofairpollutants
(Consultation Draft)
This standard specifies the establishment and classification of a local air pollutant emission standard system, the basic principles, working procedures, standard text structure and technical content requirements for standard formulation, and the basic technical methods for determining emission limits. Basic requirements for local standard filing.
This standard applies to the formulation and revision of local air pollutant emission standards and the management of the filing of local air pollutant emission standards.
The content of this standard refers to the following documents or clauses therein. For undated references, the valid version is applicable to this standard.
HJ168 Environmental Monitoring and Analysis Method Standards Technical Guidelines
HJ565 Environmental Protection Standards Compilation and Publication Technical Guide
HJ ������ Principles and methods for setting national air pollutant emission standards
HJ ������ Guidelines for compiling guidelines on best available techniques for environmental protection
`` Administrative Measures for the Preparation and Revision of National Environmental Protection Standards '' (National Environmental Regulation Science and Technology (2017) No. 1)
"Administrative Measures for the Recording of Local Environmental Quality Standards and Pollutant Discharge Standards" (Order of the Ministry of Environmental Protection No. 9)
The following terms and definitions apply to this standard.
3.1 Air Pollutants emission standard
In order to prevent environmental pollution, achieve environmental air quality standards, protect human health and the ecological environment, and combine technical and economic conditions and environmental characteristics, limit the types, concentrations, or quantities of atmospheric pollutants discharged into the environment or other factors that cause harm to the environment. The code of conduct that should be followed for various air pollutant discharge activities formulated in accordance with the law is compulsory.
3.2 local airpollutantsemission standard
The people's governments of provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the Central Government have formulated air pollutant emission standards in order to achieve environmental quality standards, prevent and control environmental pollution, protect human health and the ecological environment, and combine technical and economic conditions and environmental characteristics. The local air pollutant emission standards shall be reported to the competent department of environmental protection under the State Council for the record.
3.3 factory boundary enterpriseboundary
Legal boundaries of industrial enterprises. If the boundary cannot be determined, it refers to the actual boundary.
3.4 fugitiveemission
Air pollutants are not discharged through the exhaust canister, and are discharged into the environment through gaps, vents, and similar openings (holes).
3.5 Existing Enterprise Existing Facility
An industrial enterprise or production facility that has been put into production or that the environmental impact assessment document has passed the review before the date of implementation of the emission standard.
3.6 newfacility
Newly constructed, rebuilt and expanded industrial enterprises or production facilities construction projects whose environmental impact assessment documents have passed the review from the date of implementation of the emission standards.
3.7 Special emission limit for airpollutants
In order to prevent and control regional air pollution, improve environmental quality, and further reduce the emission intensity of air pollution sources, the use of internationally leading emission control technology and stricter control of air pollution emission regulations have established and implemented air pollutant emission limits applicable to key areas.
3.8 Air Pollutants Emission Standard For Industry
Air pollutant emission standards applicable to a particular industry are also called industry-applicable air pollutant emission standards.
3.9 Airpollutantsemission standard for generalfacilities
Applicable to air pollutant emission standards for general equipment, general operating processes, etc. in multiple industries. General air pollutant emission standards include boilers, electroplating, foundry, industrial furnaces, and malodorous air pollutant emission standards.
3.10 integrated airpollutantsemission standard
Air pollutant emission standards applicable to pollution sources in other industries that do not have industrial and general air pollutant emission standards.
4.1 The local air pollutant emission standards and the national air pollutant emission standards together constitute a system of air pollutant emission standards applicable to the locality, and the local air pollutant emission standards are given priority.
4.2 The local government shall establish a local air pollutant emission standard system with clear objectives, clear boundaries, and systematic science according to the principle of achieving the ambient air quality standards, according to the actual conditions of local air pollutant emissions and the national air pollutant emission standard system setting.
4.3 The local air pollutant emission standard system consists of three types of industry-standard, general-purpose and comprehensive emission standards. Industry-level air pollutant emission standards are only applicable to companies in specific industries, and comprehensive air pollutant emission standards are applicable to industry enterprises that do not have industry-level air pollutant emission standards. Priority will be given to the implementation of local and national industrial air pollutant emission standards.
4.4 General-purpose air pollutant emission standards are applicable to all industries that have corresponding emission facilities or pollutant emission behaviors. The industry-type air pollutant emission standards do not stipulate the general emission facilities of boilers, electroplating, industrial furnaces, odors, and casting Emission control requirements.
4.5 The people's governments of provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the central government may formulate local air pollutant emission standards for items that are not specified in the national air pollutant emission standards; Air pollutant emission standards Local air pollutant emission standards.
5.1 Local air pollutant emission standards shall be formulated in accordance with the law. The technical requirements specified in the standards shall comply with the requirements of national environmental protection laws and other relevant laws and regulations, and meet environmental impact assessments, environmental protection taxation of pollution permits, and environmental law enforcement. Management requirements.
5.2 Local air pollutant emission standards should be formulated in accordance with national environmental air quality standards and local environmental air quality planning goals, combined with local economic affordability and technical level, and the emission standards formulated should be stricter than the corresponding national air pollutant emission standards .
5.3 Comprehensive and in-depth basic data collection and on-site investigation should be carried out. If necessary, systematic on-site measurement should be carried out to truly reflect the characteristics of air pollutant emissions from the emission source, and it is possible to objectively and fairly formulate emission standards.
5.4 The production and emission control technologies shall be classified and classified, and various standards for emission limits shall be clarified, so that the formulated emission standards are technically feasible, economically reasonable, and operable.
5.5 The formulated local air pollutant emission standards shall be coordinated with the national air pollutant emission standards and other related environmental protection standards; there are perfect monitoring requirements, and the supporting monitoring method standards can meet the implementation of the standards and require manual Contents of compliance determination of monitoring data and online monitoring data.
5.6 The experience of drawing up and revising air pollutant emission standards in China and developed countries, regions and organizations should be fully absorbed to make the developed emission standards advanced.
6.1 With reference to the "Administrative Measures for the Preparation and Revision of National Environmental Protection Standards" (National Environmental Regulation Science and Technology (2017) No. 1) and the "Administrative Measures for the Recording of Local Environmental Quality Standards and Pollutant Discharge Standards" (Order of the Ministry of Environmental Protection No. 9), The working procedures for the formulation of air pollutant emission standards are divided into the opening of the argumentation stage, the consultation stage, the submission stage, the approval stage, the numbering and release stage, and the filing stage.
6.2 Demonstration stage. The project undertaking unit establishes a standard preparation team to prepare a report on the opening of the title; conducts the project opening of the reasoning to determine the scope of application of the standard, the technical route and work plan for the standard preparation.
6.3 Solicitation of opinions. The standard preparation team carried out the work according to the work plan determined by the opening report argumentation, and prepared the standard consultation draft and preparation instructions. Technical review of drafts of proposed standards and drafting instructions. After passing the technical review, solicit opinions from relevant units and the public, and solicit opinions from relevant departments of the Ministry of Environmental Protection.
6.4 Submission phase. The standard preparation group summarizes and processes the feedback opinions and suggestions, revises the standard solicitation draft and preparation instructions, forms the standard submission draft and preparation instructions, and carries out technical review of the standard submission draft and preparation instructions.
6.5 Approval stage. The standard preparation team compiles drafts of standard reports and preparation instructions. The standard administrative review shall be carried out, and the opinions of the competent national environmental protection department shall be sought before submission for approval.
6.6 Numbering and release stage. After approval by the provincial people's government, the standard numbering and issuance will be processed.
6.7 Recording stage. After the standards are published, they are reported to the national environmental protection authority for record.
7.1 Standard text structure
The structure of local air pollutant emission standards mainly includes the cover, table of contents, preface, standard name, scope of application, normative references, terms and definitions, requirements for pollutant emission control, requirements for pollutant monitoring, requirements for determination of compliance, implementation and supervision.
7.2 Determination of technical content
The technical content in the standard text, especially the scope of application of the standard, special emission control requirements for newly-built enterprises and air pollutants, factory boundary and fugitive emission control requirements, pollutant monitoring requirements, and requirements for judging standards should be strictly referred to the National Air Pollution The requirements specified in the Principles and Methods for the Establishment of Emission Standards are determined.
7.3 Determination of emission limits
7.3.1 The limits of local air pollutant emission standards should be implemented in accordance with national environmental air quality standards, local air environmental quality planning target requirements, acceptable levels of toxic and hazardous pollutants, combined with the best available technical level, relevant domestic and international emission standards, and standards. Various factors such as environmental and economic benefits and economic and technical feasibility are comprehensively considered and determined.
7.3.2 The local air pollutant emission standard limit should be stricter than the national air pollutant emission standard limit that needs to be implemented and cannot be wider than the air pollutant emission limit established in accordance with the technical methods in Chapter 8 of this standard.
7.4 Determination of monitoring requirements
7.4.1 National environmental monitoring method standards should be selected for pollutant discharge monitoring. For pollutant projects for which there is no national environmental monitoring method standard, the monitoring analysis method can be specified in the appendix of the standard text after experimental verification and technical demonstration, or its emission limit will be implemented after the national environmental monitoring method standard is issued.
7.4.2 It is stipulated in the standard appendix that the monitoring and analysis method shall meet the basic requirements of HJ168, and the lower limit of measurement shall not be lower than the requirement for accurate and quantitative measurement of pollutant control items, and the precision and accuracy shall not be lower than the corresponding general method requirements.
7.5 Determination of compliance requirements
7.5.1 When formulating local air pollutant emission standards, comprehensive collection of pollutant emission data of existing local enterprises or production facilities should be conducted. After deducting emission data from abnormal operating conditions, a thorough and systematic analysis of the hourly and daily averages of pollutants should be conducted. Based on the statistical distribution rules of weekly average, weekly average, monthly average concentration, and seasonal average concentration, the requirements for reaching the standard are put forward.
7.5.2 Combined with the relevant national standards for air pollutant emission standards related to the requirements of judging standards, and based on international standards for air pollutant emission standards in the same industry, determining the requirements for local standards, but should not Wider than the requirements for determining compliance in the national emission standards.


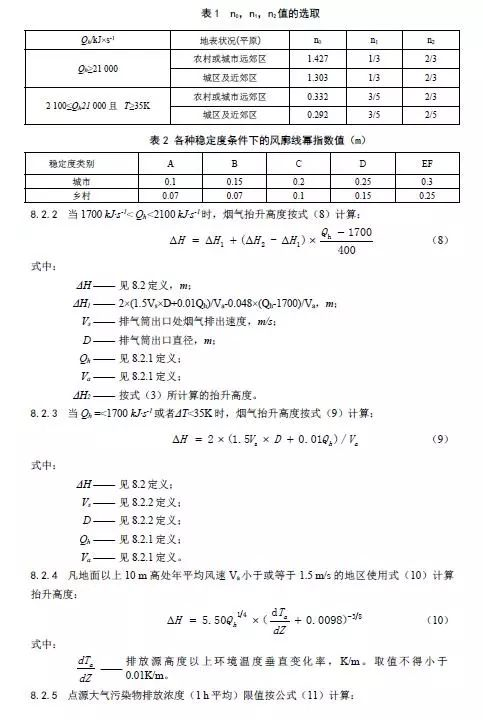

9.1 Prediction of pollutant emission reduction and environmental quality improvement effects
9.1.1 Based on national and local industrial policies, industry access conditions, environmental policies, and other requirements, analyze the development trend of local enterprises (devices) for which applicable standards are developed for 3-5 years, mainly including various production processes each year The growth rate of installations, product capacity, output trends, pollution control technologies and energy structure adjustments.
9.1.2 Based on the trend of local product output changes, the annual emissions of each pollutant under the current standards of existing enterprises and newly-built enterprises and all enterprises in the next 3-5 years should be analyzed. Then analyze the annual emissions of each pollutant when existing local enterprises and new and all enterprises in the next 3-5 years implement the new standards. Calculate annual reductions in pollutant emissions and reduction ratios based on emissions from current and new standards.
9.1.3 For industries with large emissions of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds, the effect of the implementation of the standard on the local ambient air quality should be predicted. It should be based on the premise that the prescribed pollutant emission limit is met, and in combination with industry development planning, design different emission scenarios for the next 3-5 years and calculate emissions reductions, and predict the contribution of the implementation of standards to the improvement of ambient air quality.
9.2 Economic Cost Analysis
9.2.1 Based on the classification and grading technology, the existing enterprises and newly-built enterprises will meet the technical standards for pollutant emission standards to determine the emission control technologies or technology combinations applicable to various local enterprises. Based on the collected investment data and operating data of each emission control technology, the fixed investment cost and annual operating cost of each emission control device are calculated.
9.2.2 Comprehensively grasp the level of pollutant emission control of each type of local enterprise or device, and determine the number of emission control devices that need to be retrofitted and newly added by existing enterprises. Based on the fixed investment cost and annual operating cost of each typical emission control device, calculate the fixed investment cost and operating cost that local enterprises need to increase, as well as the increase in fixed investment and annual production and operating costs.
9.2.3 For the implementation of new emission standards, promote the popularization of clean production processes in the industry, reduce material consumption, energy consumption, increase product output, etc., the economic benefits of the implementation of the standards should be analyzed, including the number of cleaner production process devices and Cost, the economic benefits of enterprises across the industry as a result of reducing material consumption, energy consumption and increasing product output, as well as economic costs after netting out production costs or deducting economic benefits.
The main contents of the standard preparation instructions include the project background, industry overview, the necessity analysis of the standard system (revision), the analysis of industrial production and pollution and pollution control technology analysis, the environmental impact analysis of toxic and harmful pollutants emitted by the industry, the main technical content of the standard, Research on relevant external emission standards, environmental benefits and economic and technical analysis of standards implementation, comments on standards, technical review and administrative review.
11.1 After the provincial, autonomous region, or municipality ��s people ��s government or its entrusted environmental protection administrative department has issued local air pollutant emission standards, it shall comply with the ��Administrative Measures for Recording Local Environmental Quality Standards and Pollutant Emission Standards�� (Order of the Ministry of Environmental Protection No. 9) for filing with the Ministry of Environmental Protection.
11.2 The local air pollutant emission standards may be consulted by the Ministry of Environmental Protection before seeking comments and administrative approval.