-
Factory Environmental Governance Comprehensive Solution Provider
-
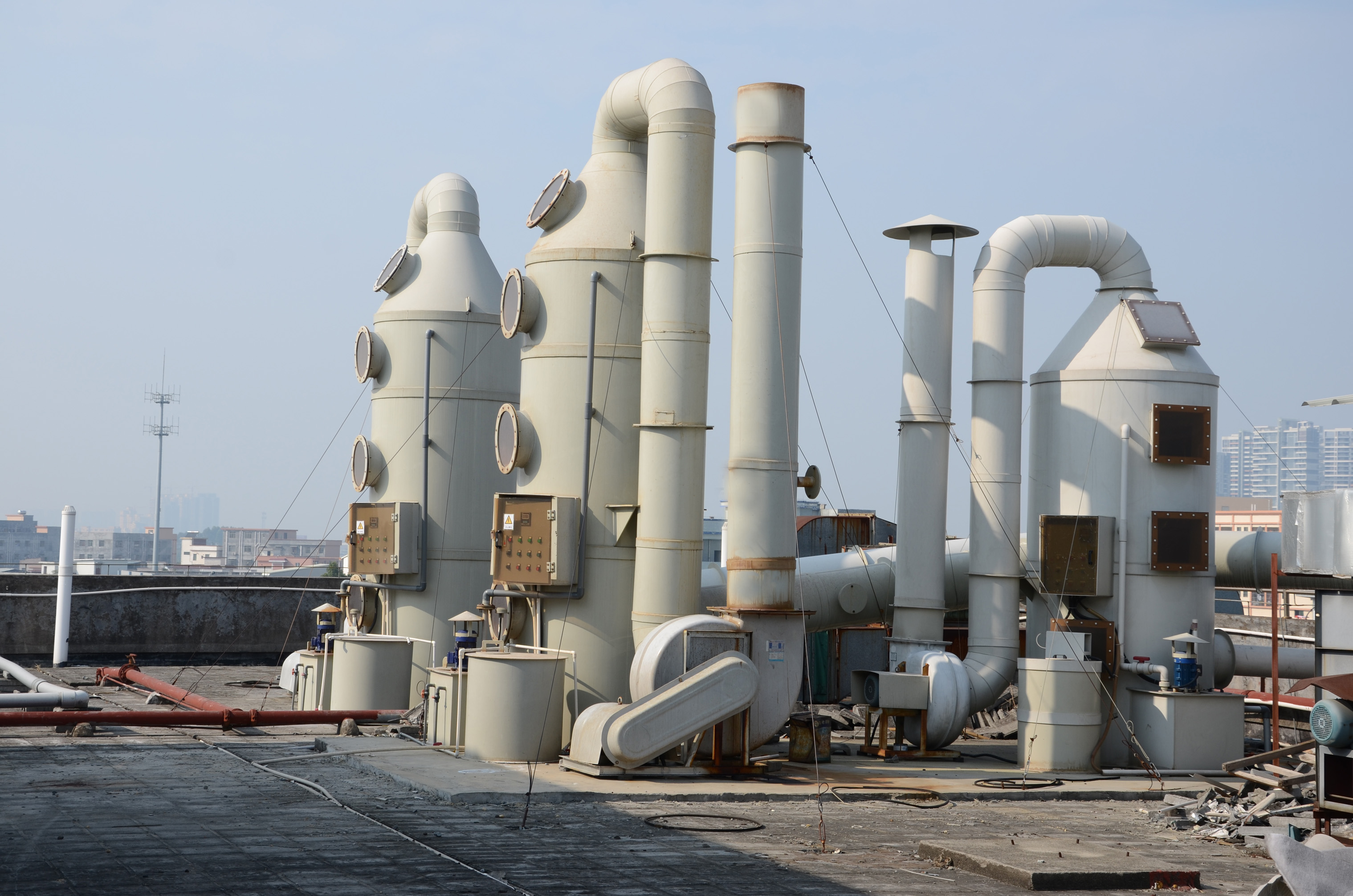
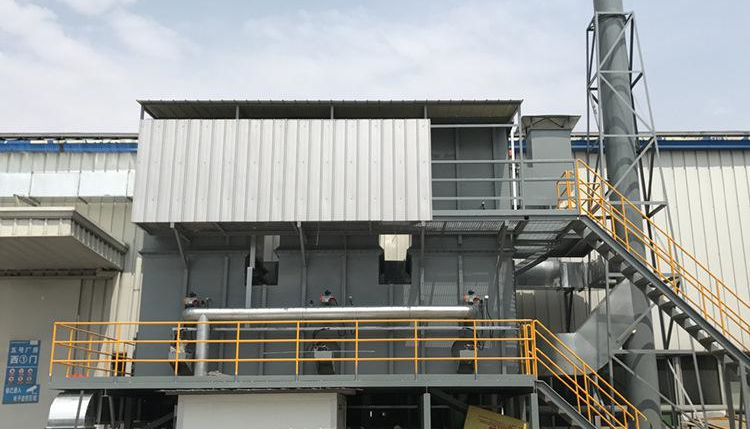
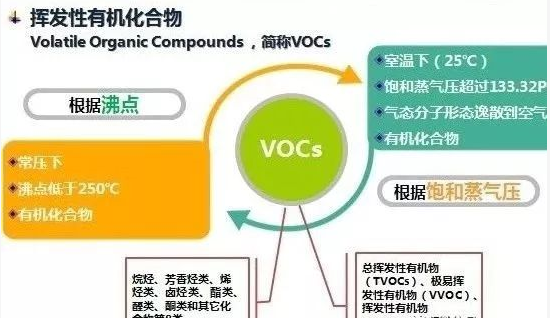
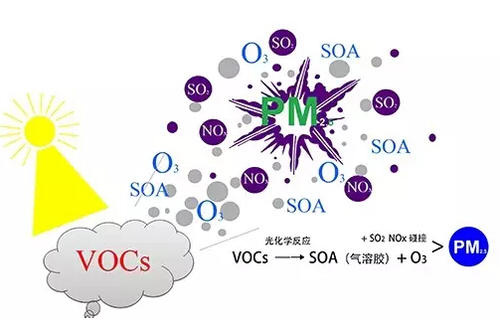
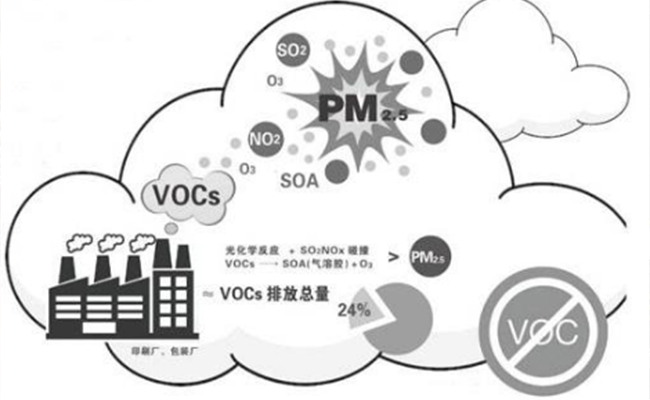
Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment

Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment
China ’s air pollutant emission standards have begun in 1973. After 44 years of development, they have experienced the initial stage, initial formation, system adjustment, and rapid development. At present, relatively complete air pollutant emission standards have been initially formed The system basically covers the key sources of air pollutant emissions in China and plays an important role in China's air pollutant emission management.

(1) The starting stage. The “Trial Standard for Industrial“ Three Wastes ”Emissions” (GBJ 4-73), jointly issued by the former State Construction Commission, the former State Planning Commission, and the Ministry of Health in 1973, is China's first environmental protection standard, which stipulates 13 types of atmospheric pollutants. Emission rate or concentration, which played a significant role in the control of air pollutant emissions in the early days of China's environmental protection work.
(2) Initial formation stage. In 1979, China's first "Environmental Protection Law" (trial) was promulgated and implemented. In 1987, China's first "Air Pollution Control Law" was promulgated and implemented. In 1989, the revised "Environmental Protection Law" was officially implemented. During this period, in accordance with the aforementioned laws, China established and implemented a series of atmospheric environmental protection management systems. The legal status and role of environmental quality standards and emission standards were further clarified. Further strengthened. Aiming at the problems in the implementation of GBJ 4-73, such as the lack of industry specificity and excessively wide emission limits, the state began to separate the emission control of industries and production facilities such as chemical industry and industrial boilers from GBJ 4-73. By 1991, a total of 14 industry and general facilities air pollution emission standards were revised, such as the “Boiler Smoke Emission Standard” (GB / T 3841-1983) issued in 1983, and Emission Standards "(GB 13223-1991). Since the main air pollutants controlled in China during this period were soot and dust, the pollutants specified in these emission standards were also mainly soot and dust.
(3) System adjustment phase . During the initial formation of the emission standards system, China has formulated a series of emission standards, but the problem of cross-standards in the implementation process is more prominent. Therefore, around 1989, China began to systematically sort out the air pollutant emission standard system, and in accordance with the requirements of environmental management, established a "comprehensive emission standard as the main body, supplemented by industry-type emission standards. The emission standard system framework of “emission standard priority” has significantly changed the air pollutant emission standard system. Up to 1996, there were 7 emission standards for air pollutants from fixed sources, including: "Integrated Emission Standards for Air Pollutants" (GB 16297-1996), as well as malodor, thermal power plants, boilers, coke ovens, cement industry, industrial furnaces, etc. Air pollutant emission standards. Thermal power, cement, coking and other industries implement special applicable air pollutant emission standards. Pollutants not specified in the standards do not implement the Comprehensive Air Pollutant Emission Standards. All other types of pollution sources shall be implemented in accordance with GB 16297-1996. In the required non-cross implementation, the emission management of malodorous pollutants is an exception. The emission standards of malodorous pollutants are not only cross-implemented with the above-mentioned industry-type emission standards, but also with the comprehensive emission standards. Odor pollutants not specified in the comprehensive and comprehensive emission standards are subject to the odor pollutant emission standards, so the odor pollutant emission standard is a general-purpose emission standard.
(4) Rapid development stage. GB 16297-1996 has a wide range of applicable pollution sources and plays an important role in the management of air pollutant emissions. However, there are also problems such as poor applicability and poor pertinence of emission control requirements. The amendment to the "Air Pollution Prevention and Control Law" of China in 2000 clearly stipulated that "exceeding the standards and violating the law", which conferred a very high legal status on air pollutant emission standards, which became the boundary between "legal" and "illegal". In particular, the "Decision of the State Council on Implementing the Scientific Outlook on Development and Strengthening Environmental Protection" and the Sixth National Environmental Protection Conference put forward higher requirements for environmental standard work, and it is imperative to vigorously promote the formulation of industry-based emission standards. Therefore, in the "Eleventh Five-Year", "Twelfth Five-Year" and "Thirteenth Five-Year" environmental protection standard planning, efforts were made to formulate industry-based pollutant discharge standards, and steel, coal, thermal power generation, and pesticide And revision tasks of pollutant emission standards in key industries such as China ’s non-ferrous metals, building materials, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, chemicals, oil and gas, machinery, textile printing and dyeing, etc., increasing the coverage of industry-based emission standards, and gradually reducing the general and comprehensive pollutant emission standards — 4 — Quasi-applicable scope. In addition to controlling conventional pollutants, more attention is paid to the control of toxic pollutants, such as heavy metals, VOCs, and greenhouse gas emissions.

China's current system of emission standards for air pollutants from fixed sources is mainly composed of industry-type, general-purpose, and comprehensive air pollutant emission standards. Industry-specific air pollutant emission standards refer to the air pollutant emission standards applicable to companies in a particular industry, and are also referred to as industry-specific air pollutant emission standards. General air pollutant emission standards refer to air pollutant emission standards for general equipment, general operating processes, and general pollutants applicable to multiple industries, mainly including boiler, industrial furnace and odor air pollutant emission standards. Comprehensive air pollutant emission standards refer to air pollutant emission standards applicable to all industry emission sources, and are also known as industry-wide pollutant emission standards.
Pollution sources controlled by industry-type emission standards are usually controlled by industry-type standards and general-purpose standards; pollution sources that are not controlled by industry-type emission standards are usually controlled by comprehensive emission standards and general-purpose emission standards. Up to now, China has 46 emission standards for fixed-source air pollutants (see Table 1), of which 41 are industry-type emission standards, 4 are general-purpose emission standards, and 1 is the comprehensive emission standard.
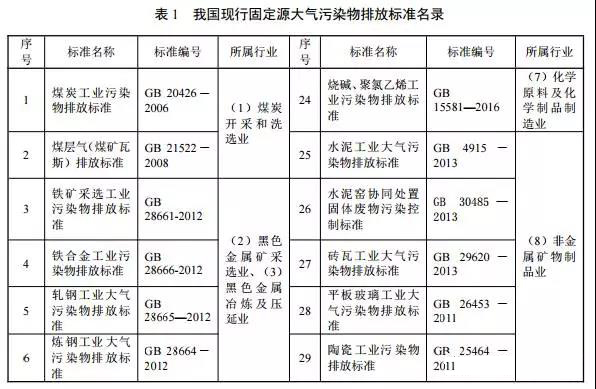
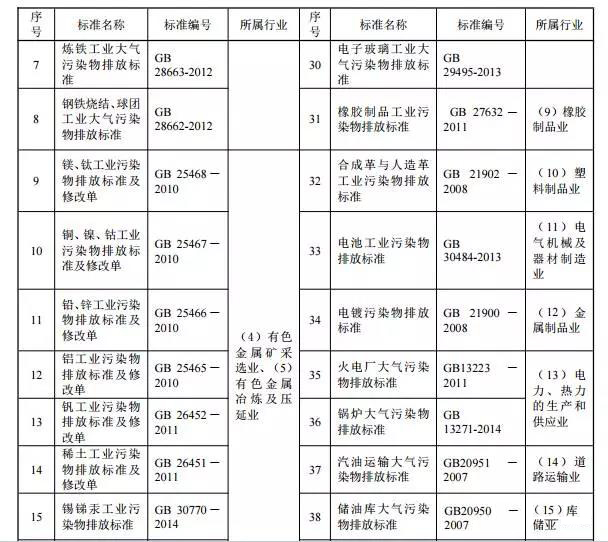
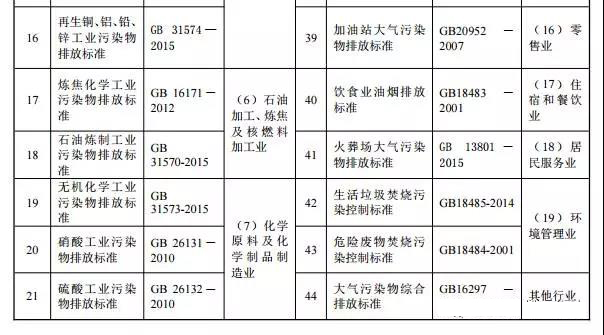
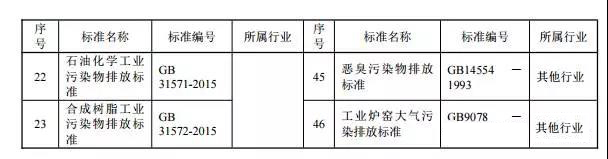
The Ministry of Environmental Protection is organizing efforts to formulate and revise 31 fixed-source air pollutant emission standards (see Table 2), of which 27 are industrial-type emission standards, and the general-purpose emission standards are mainly VOC fugitive emissions, casting, and foul air. Emission standards, 1 comprehensive emission standard.