-
Factory Environmental Governance Comprehensive Solution Provider
-
Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment

Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment
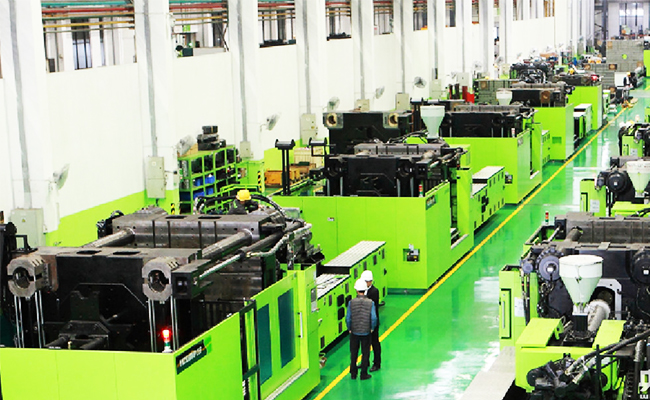
Injection molding is a process commonly used in modern plastic processing and production. The products usually use rubber injection molding and plastic injection molding. During the use process, the exhaust gas generated by this process can have a damaging effect on the atmosphere if it is not effectively treated. The treatment of injection waste gas mainly includes methods such as active adsorption, UV photolysis, plasma, and incineration.
I. Sources and hazards of waste gas in the injection molding industry
The injection molding machine generates organic waste gas during the injection molding heating process, and its main components are dust particles, non-methane total hydrocarbons and other harmful substances. The exhaust gas has an irritating odor and is slightly toxic, which has great harm to human health. The fugitive emissions of styrene, toluene, and organic waste gas will cause serious pollution to the environment and cause great damage to human health. Therefore, the waste gas of the production line of the plastic factory has to be treated carefully. Exhaust gas from injection molding contains a lot of harmful components to the human body, such as acrylonitrile, non-methane total hydrocarbons, vinyl chloride, etc. If it is not treated in a timely and effective manner, it will pose a huge threat to the health of the workshop staff and cause environmental harm damage.
Second, the waste gas treatment method of injection processing industry
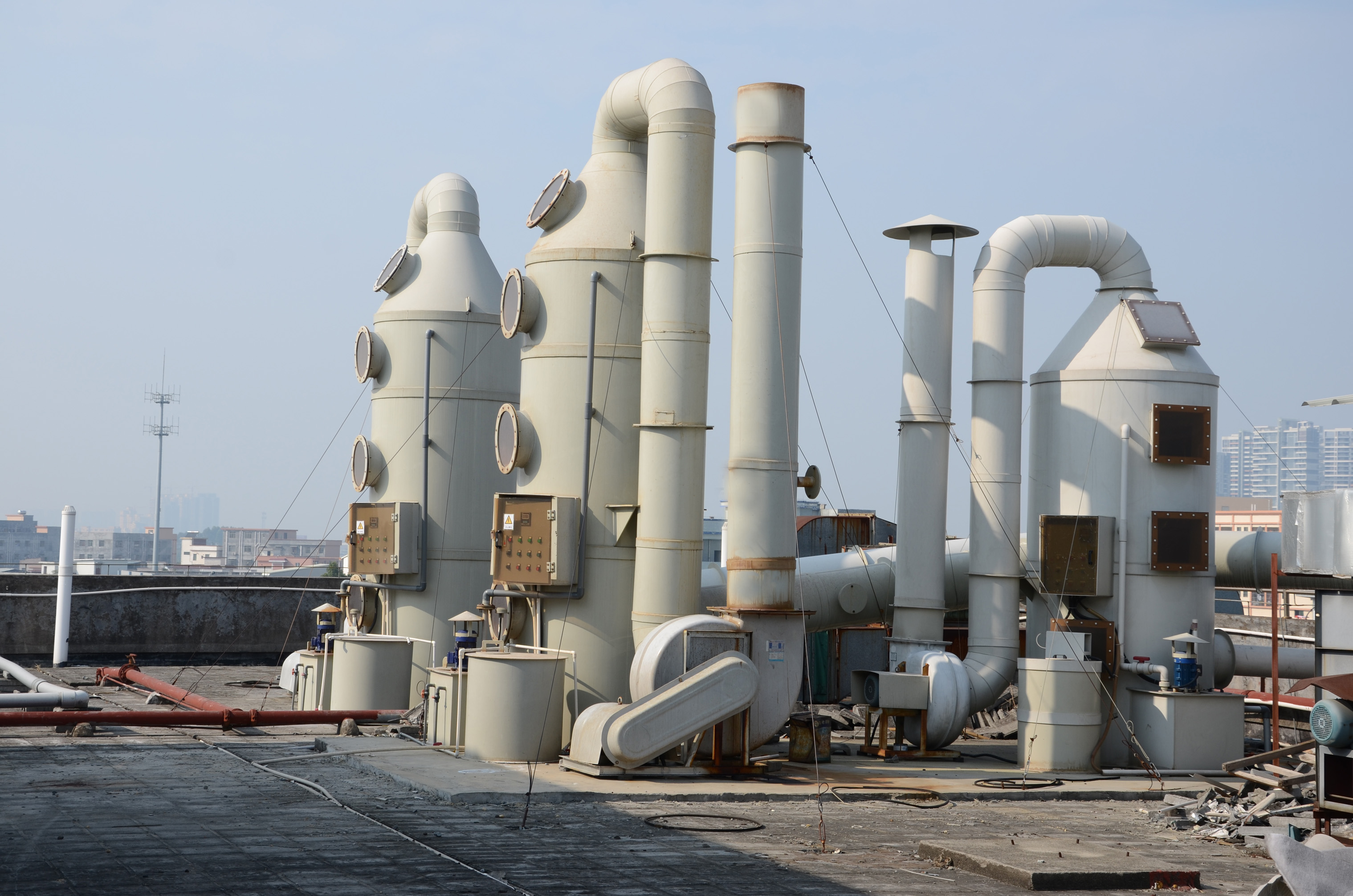
Activated carbon adsorption method
(1) Activated carbon adsorption is a commonly used recovery technology for waste gas treatment in the injection molding industry. The principle is to use the porous structure of adsorbents (granular activated carbon and activated carbon fibers) to capture VOCs in the exhaust gas. The organic waste gas containing VOCs is passed through an activated carbon bed, and VOsC therein is adsorbed by an adsorbent, and the injection waste gas is purified and discharged into the atmosphere.
(2) When the carbon adsorption reaches saturation, the saturated carbon bed is desorbed and regenerated; VOCs are blown off when steam is introduced to heat the carbon layer, and form a steam mixture with water vapor, leaving the carbon adsorption bed together, and using a condenser The vapor mixture is cooled to condense the vapor into a liquid. If the VOCs are water-soluble, the liquid mixture is purified by distillation; if they are water-insoluble, the VOCs are directly recovered by a decanter. Because the tribenzene used in the coating is incompatible with water, it can be directly recovered.
(3) Activated carbon adsorption technology is mainly used in the case where the components in the exhaust gas are relatively simple and the value of organic matter recycling is high. The size and cost of the exhaust gas treatment equipment are proportional to the number of VOCs in the gas, but relatively independent of the exhaust gas flow; therefore, Carbon adsorption beds are more inclined to dilute atmospheric flows, and are generally used when the VOCs concentration is less than 5000PPM. It is suitable for spray painting, printing and adhesives, where the temperature is not high, the humidity is not large, and the exhaust volume is large, especially for the purification and recovery of halogen-containing compounds.
2.UV photolysis method
UV photolysis technology uses special ultraviolet wave bands to rupture injection molding exhaust gas molecules and break their molecular chains. At the same time, it decomposes water and oxygen in the air to make them highly active ozone or free hydroxyl groups, thereby oxidizing exhaust gas molecules. Generates water and carbon dioxide. Adding a catalyst can improve the reaction rate and the efficiency of processing injection waste gas, thereby achieving the purpose of purifying the waste gas. Photocatalytic oxidation technology is a VOCs treatment method with a wide application range and mature technology.
3. Plasma method
Plasma technology has a wide range of applications and high purification efficiency, especially for multi-component malodorous gases that are difficult to handle by other methods, such as chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the one-time investment is huge and there are certain security risks. The exhaust gas of the injection molding machine is activated by plasma, dissociated and activated, and then the activated exhaust gas is catalyzed and oxidized with oxygen in the exhaust gas by high-energy rays on the surface of the rare metal oxide, and finally converted into carbon dioxide and water and other substances.
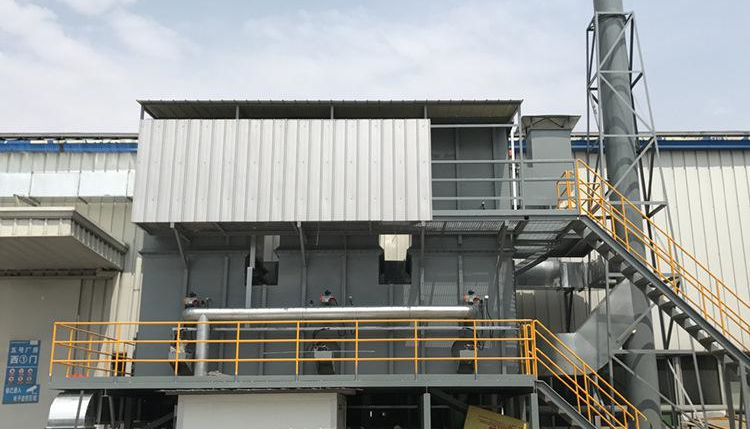
4. Incineration
(1) The incineration technology includes high-temperature incineration and catalytic combustion. It is relatively mature and widely used in foreign countries. It is suitable for processing high-concentration, small-air-volume VOCs, and requires high safety and airtightness of the entire technology. When dealing with large air volume and low concentration of VOCs, it is necessary to pre-process it with related concentration technology.
(3) High-temperature incineration is the combustion treatment of organic components in exhaust gas under high temperature conditions to generate carbon dioxide and water. Catalytic combustion is the use of a catalyst to reduce the temperature required for the reaction during combustion, so that the exhaust gas can be burned at room temperature to generate carbon dioxide and water.