-
Factory Environmental Governance Comprehensive Solution Provider
-
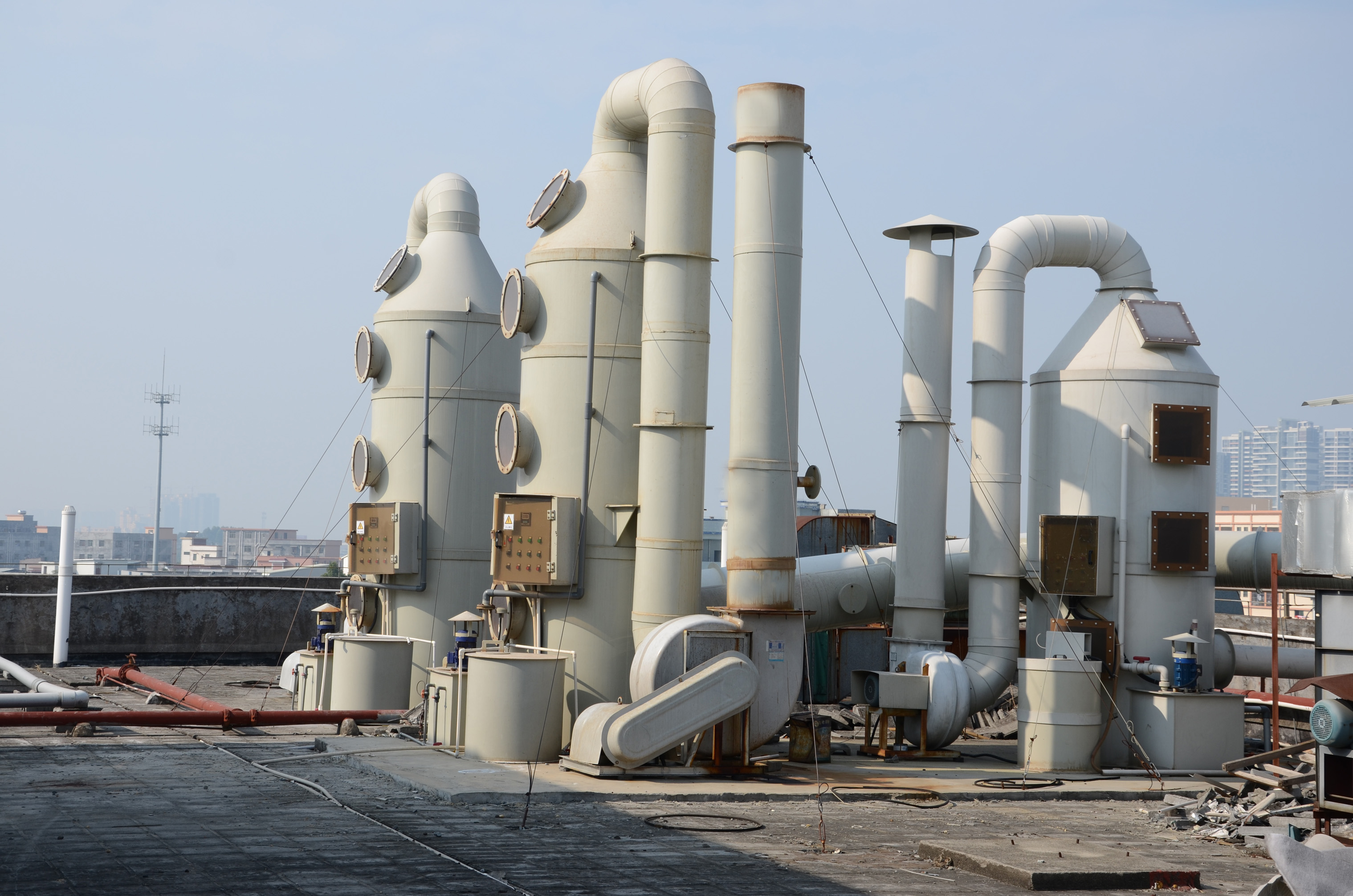
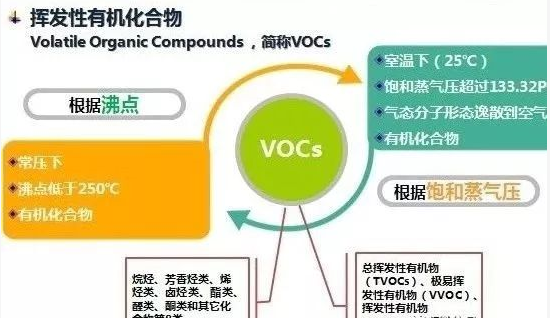
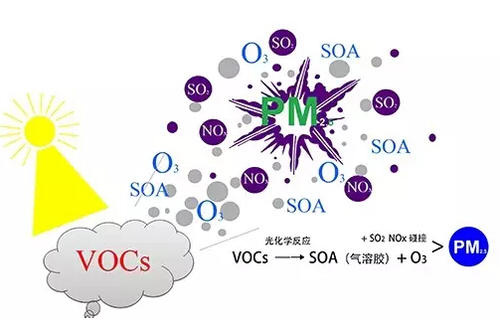
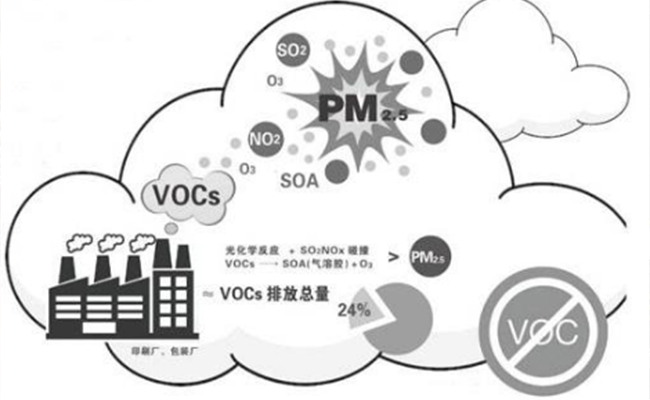
Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment

Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment
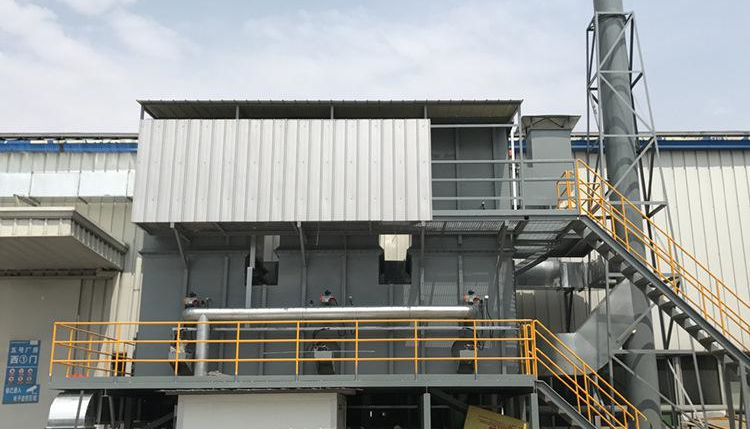
Combustion or recovery of high-volume, low-concentration organic waste gas not only requires very large-scale equipment, but also causes huge operating costs. For this problem, by using a zeolite molecular sieve adsorption and concentration device , organic waste gas with a low concentration and large air volume can be concentrated into a small concentration with a high air volume , thereby reducing equipment investment costs and operating costs, thereby achieving economical and effective organic waste gas treatment.
The zeolite runner organic exhaust gas purification technology is a technology that uses zeolite molecular sieve adsorbent to adsorb and purify VOCs in exhaust gas. Zeolite molecular sieves are crystalline aluminosilicates, which are widely used in the field of exhaust gas treatment due to their regular crystal structure, uniform pore distribution, and adjustable surface properties.
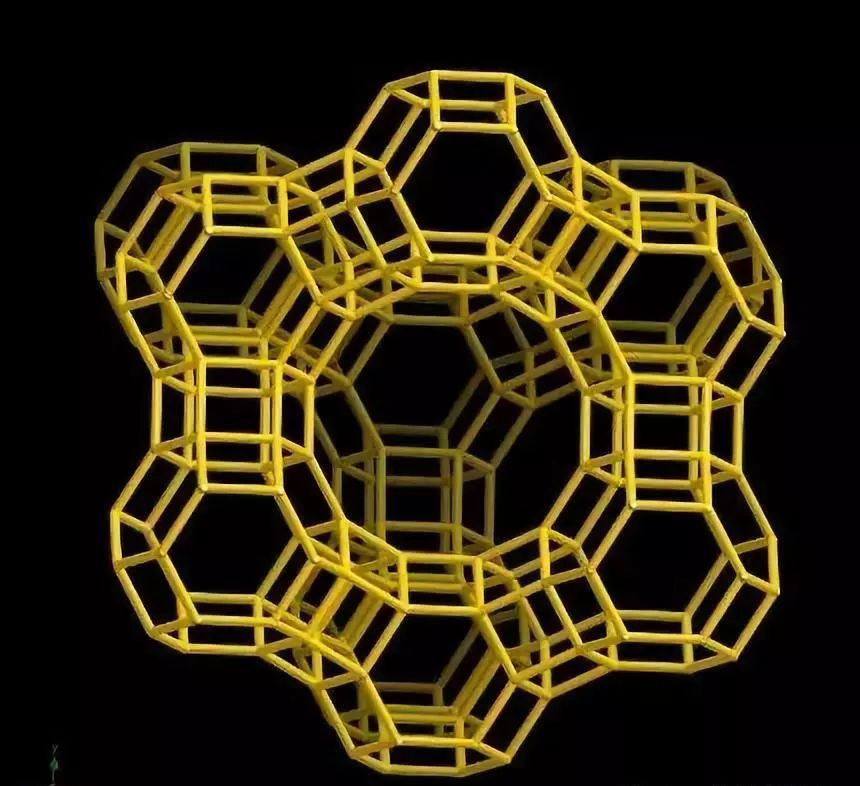

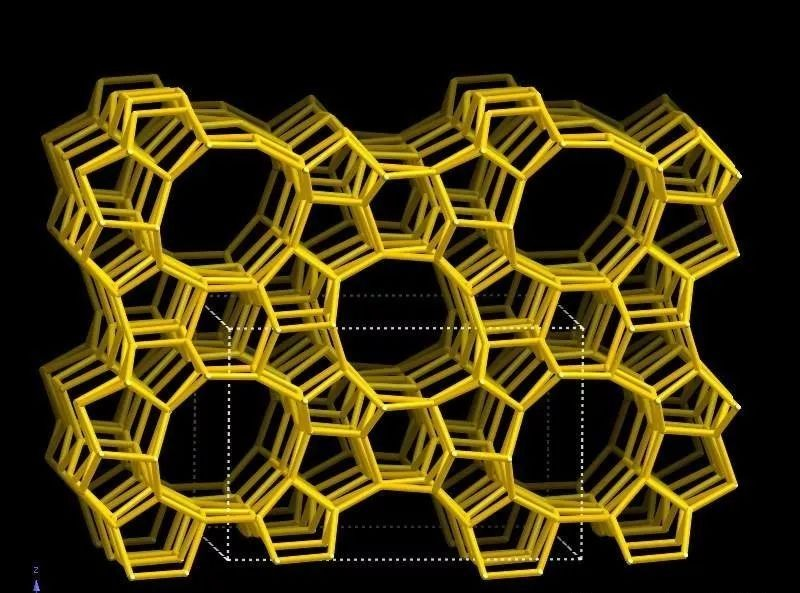
Figure Schematic structure of zeolite molecular sieve
Hydrophobic silicalite adsorbent exhibits strong hydrophobic / lipophilic characteristics, has uniformly-sized pores, large specific surface area (500 ~ 1000�O / g), and large adsorption capacity, and can be used to adsorb and remove many organic molecules from exhaust gas. , Is a new type of environmentally friendly material.
On the molecular sieve runner, olefins, organosiloxanes, and macromolecular substances with a boiling point above 260 �� C may cause permanent damage to the runner.
The substances that the runner cannot handle, the substances that are not allowed to enter the runner, and the substances that are restricted from entering the runner are listed below. The list is as follows:
Table Substances that the runner cannot handle
status | Substance composition | phenomenon |
Difficult to adsorb substances | Methanol | Strong polarity does not adsorb |
Cyclohexane | Not easy to adsorb on structure | |
Formaldehyde, other low boiling point substances | Low boiling point is not easy to adsorb | |
Not easily desorbed | Oil mist / tar mist | Not easy to detach |
Plasticizers (DEP, DOP, etc.) | High boiling point is not easy to desorb | |
Terpineol | React and accumulate in pores | |
Monomer chlorinated vinyl, acrylonitrile, isocyanate, other polymerizable substances | Polymerizable substance | |
Monoethanolamine (MEA) | Low steam pressure makes it difficult to desorb | |
Other amines | Changing traits is not easy to detach | |
High boiling point substances above 200 �� C | Not easy to detach | |
Substances with a vapor pressure below 20 Pa (at20 �� C) | Not easy to detach | |
Molecular sieve degradation | Acid and alkaline substances | Zeolite degradation |
coating | Covering molecular sieve produces degradation |
Table of substances that are not allowed to enter the runner
Substances not allowed to enter the runner | the reason | Content control |
Dust (calcium carbonate, titanium dioxide, white carbon black, ammonium chloride, iron oxide, etc.) | Clogged holes | <1mg / m3 |
Paint mist (mist liquid formed by spraying, resin) | Clogged holes | <0.1mg / m3 |
Polymerization monomers such as acrylic acid, acrylonitrile, butadiene | Adsorbent deactivation | <0.1mg / m3 |
Active compounds such as isocyanate and silane coupling agent | Adsorbent deactivation | <0.1mg / m3 |
Boiling point is greater than 220 �� C (diethylene glycol butyl ether, triethanolamine, phthalates, etc.) | Cannot detach | <0.1mg / m3 |
Melting point is greater than 20 �� C (phenol, naphthalene, tetramethylbenzene, etc.) | Clogged holes | <0.1mg / m3 |
HCl, Cl2, SO2, H2S, NOx, NH3 | Corrosive | PH = 4-10 |
Table restricted substances entering the runner
Substances restricting access to runners | the reason | Content control |
Styrene | Easy to aggregate | <600mg / m3 |
Easy to aggregate | <0.1mg / m3 | |
Dichloromethane, pentane, ethanol, cyclohexane | Not easy to adsorb | Designed according to efficiency requirements |
Methanol, formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, carbon disulfide | No adsorption | Designed according to efficiency requirements |
Boiling point below 40 �� C (alkanes, olefins, halogenated hydrocarbons, etc. below C4) | No adsorption | Designed according to efficiency requirements |
Xylene, Xylene, Cyclohexanone and other macromolecules | Some runners do not adsorb | Designed according to efficiency requirements |
Boiling point at 170-220 �� C (trimethylbenzene, ethylene glycol butyl ether, propylene glycol, ethylene glycol, decane, NMP, DMSO, DEF, butyrolactone, etc.) | Difficult to detach | Activated carbon filtration or high temperature regeneration |