-
Factory Environmental Governance Comprehensive Solution Provider
-
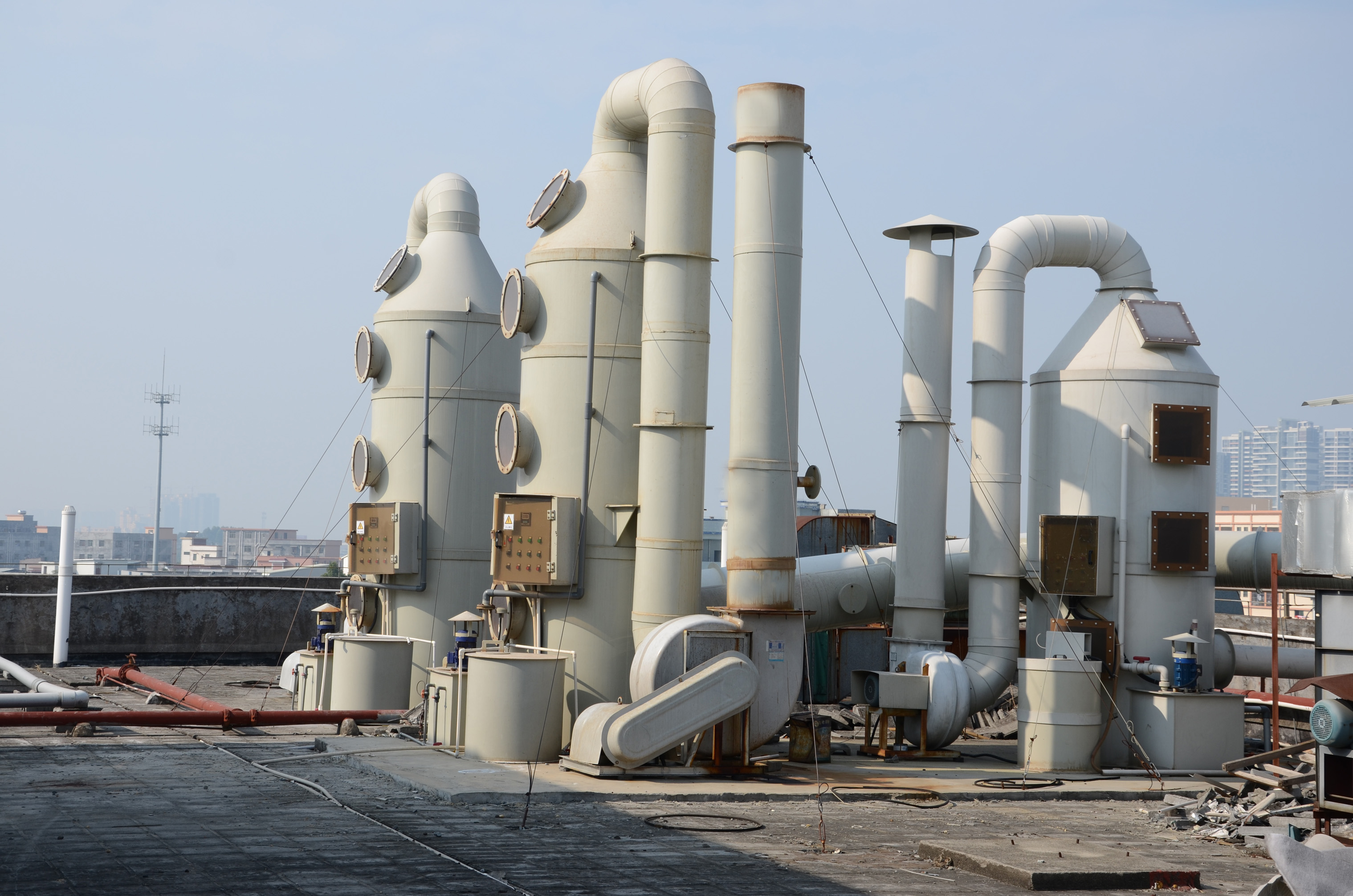
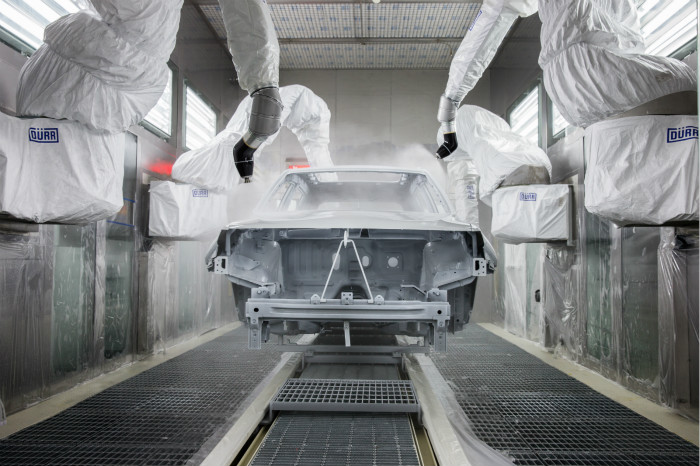
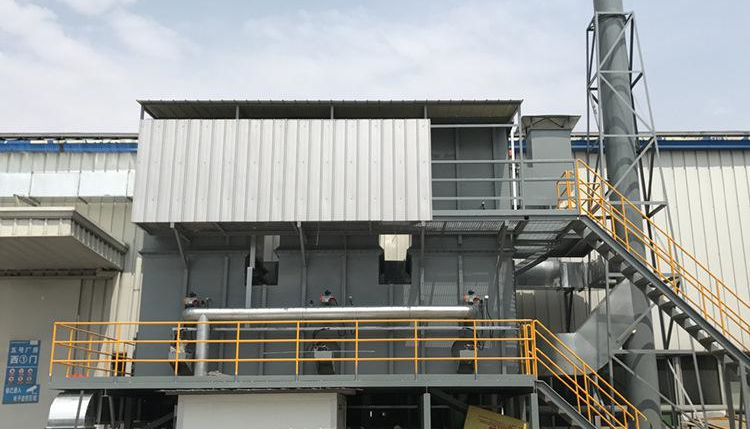
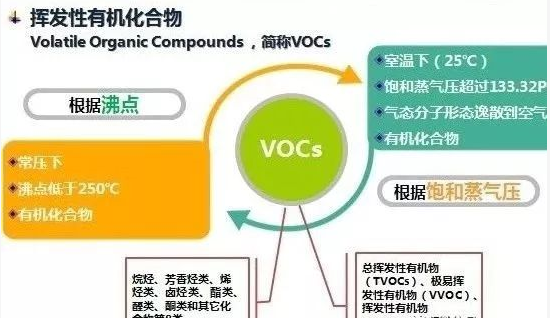
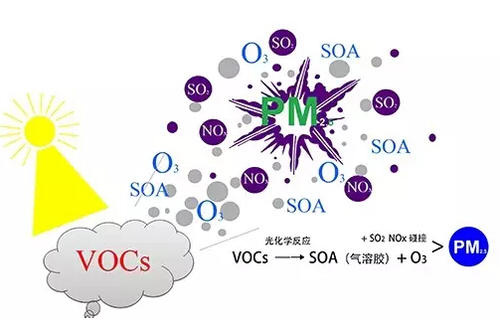
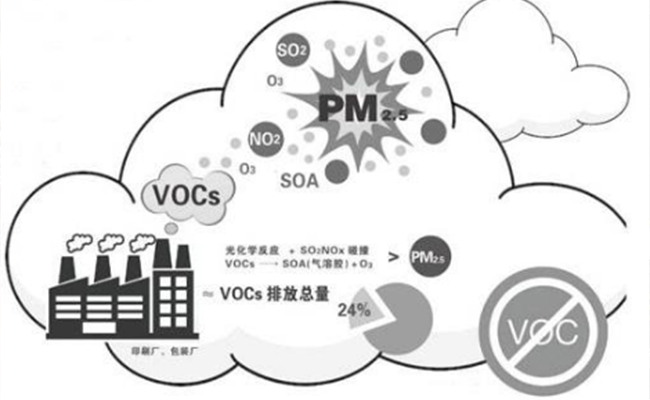
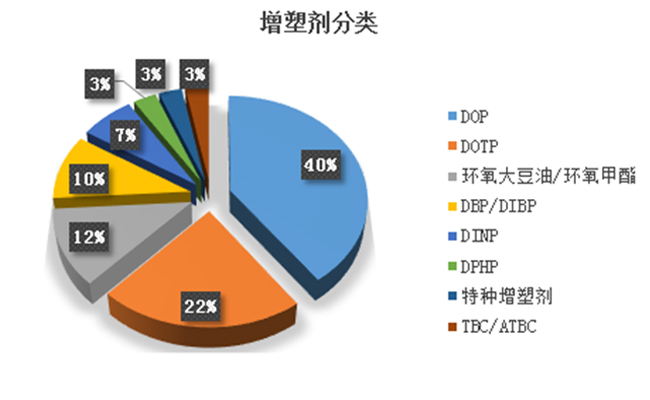
Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment

Focus on R & D and manufacturing of VOCs exhaust gas treatment equipment
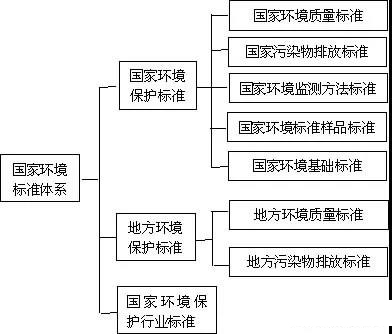
According to the "Legislative Law", the legal system framework is mainly divided into three layers: the first layer is the law, which is passed by the National People's Congress. The second layer is administrative regulations, which are divided into administrative regulations and local regulations of the State Council. The administrative regulations of the State Council are adopted by the State Council; the local regulations are adopted by the Standing Committee of the Local People's Congress. The third layer is regulations, which are divided into departmental regulations of the State Council and local government regulations. Departmental regulations issued by the State Council's constituent departments in the form of ministerial orders are issued by the local government in the form of government orders.Local regulations and local government regulations are issued by local people's congresses and local governments with legislative power. 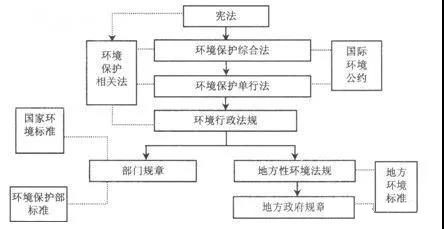
1. Law
Laws are normative documents formulated and promulgated by state organs with legislative power in accordance with legislative procedures. In China, laws are formulated and promulgated by the National People's Congress and its Standing Committee in accordance with legislative procedures. The National People's Congress formulates and revises criminal, civil, state agency and other basic laws. The Standing Committee of the National People's Congress formulates and revises laws other than those that should be formulated by the National People's Congress; during the intersessional period of the National People's Congress, it is possible to partially supplement and modify the laws formulated by the National People's Congress, It must not conflict with the basic principles of the law. The law is promulgated by a presidential order signed by the president of the country. The power to interpret the law belongs to the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress. The effectiveness of laws is higher than administrative regulations, local regulations and rules.

2:Regulations
Regulations include administrative regulations and local regulations. Administrative regulations are formulated by the State Council in accordance with the Constitution and laws, and are promulgated by the State Council by signing the Decree of the State Council. Local regulations are formulated by the people's congresses and their standing committees of provinces, autonomous regions, municipalities directly under the Central Government, and larger cities in accordance with the specific conditions and actual needs of their respective administrative regions. The names of administrative regulations are generally called "regulations", and can also be called "regulations", "methods", and so on. If the text of the administrative regulations itself needs to further clarify the boundaries or make supplementary provisions, the State Council shall interpret them. The effectiveness of administrative regulations is higher than local regulations and rules. The effectiveness of local regulations is higher than that of local and local governments.

3:Regulations
Regulations include departmental regulations of the State Council and local government regulations. Departmental rules and regulations of the State Council are formulated by the ministries and commissions of the State Council, the People's Bank of China, the Audit Office, and direct agencies with administrative functions in accordance with the laws and administrative regulations, decisions, and orders of the State Council within the authority of this department. The people's governments of the municipalities directly under the Central Government and larger cities shall be formulated in accordance with laws, administrative regulations and local regulations in the region. The rules shall be promulgated by an order signed by the head of the department or the governor, the chairman of the autonomous region and the mayor. The name of the regulations is generally called "regulations" and "methods", but not "regulations". The right to interpret the rules belongs to the rules-making body. The regulations formulated by the people's governments of provinces and autonomous regions are more effective than those formulated by the people's governments of larger cities in the administrative region. They have the same effect among departmental regulations, between departmental regulations and local government regulations, and are implemented within their respective jurisdictions. When the provisions on the same matter are inconsistent between departmental regulations, between departmental regulations and local government regulations, the State Council shall rule.